An administrator would like to securely connect to a server and forward port 8080 on a local machine to port 80 on the server. Which of the following commands should the administrator use to satisfy both requirements?
Correct Answer:
A
This command will create a local port forwarding, which means that connections from the SSH client are forwarded via the SSH server, then to a destination server. In this case, the destination server is the same as the SSH server (localhost), and the destination port is 80. The SSH client will listen on port 8080 on the local machine, and any connection to that port will be forwarded to port 80 on the server. This way, the administrator can securely access the web service running on port 80 on the server by using http://localhost:8080 on the local machine.
The other options are incorrect because:
* B. ssh -R 8080:localhost:80 admin@server
This command will create a remote port forwarding, which means that connections from the SSH server are forwarded via the SSH client, then to a destination server. In this case, the destination server is the same as the SSH client (localhost), and the destination port is 80. The SSH server will listen on port 8080 on the remote machine, and any connection to that port will be forwarded to port 80 on the client. This is not what the administrator wants to do.
* C. ssh -L 80:localhost:8080 admin@server
This command will also create a local port forwarding, but it will use port 80 on the local machine and port 8080 on the server. This is not what the administrator wants to do, and it may also fail if port 80 is already in use by another service on the local machine.
* D. ssh -R admin@server
This command is incomplete and invalid. It does not specify any port numbers or destination addresses for the remote port forwarding. It will also fail if the SSH server does not allow remote port forwarding.
References:
✑ CompTIA Linux+ Certification Exam Objectives
✑ How to Set up SSH Tunneling (Port Forwarding)
A Linux administrator is troubleshooting SSH connection issues from one of the workstations.
When users attempt to log in from the workstation to a server with the IP address 104.21.75.76, they receive the following message: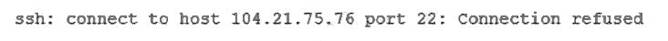
The administrator reviews the information below:

Which of the following is causing the connectivity issue?
Correct Answer:
C
The server’s firewall is preventing connections from being made, which is causing the connectivity issue. The output of iptables -L -n shows that the firewall is blocking all incoming traffic on port 22, which is the default port for SSH. The output of ssh -v user@104.21.75.76 shows that the connection is refused by the server. To resolve the issue, the administrator needs to allow port 22 on the firewall. The other options are incorrect because they are not supported by the outputs. The workstation has the correct IP settings, as shown by the output of ip addr show. The sshd service is enabled and running, as shown by the output of systemct1 status sshd. The server has the correct default gateway configuration, as shown by the output of ip route show. References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 13: Managing Network Services, pages 406-407.
A systems administrator is tasked with mounting a USB drive on a system. The USB drive has a single partition, and it has been mapped by the system to the device /dev/sdb. Which of the following commands will mount the USB to /media/usb?
Correct Answer:
A
The mount /dev/sdb1 /media/usb command will mount the USB drive to /media/usb. This command will attach the filesystem on the first partition of the USB drive (/dev/sdb1) to the mount point /media/usb, making it accessible to the system. The mount /dev/sdb0 /media/usb command is invalid, as there is no such device as /dev/sdb0. The mount /dev/sdb /media/usb command is incorrect, as it will try to mount the entire USB drive instead of its partition, which may cause errors or data loss. The mount -t usb
/dev/sdb1 /media/usb command is incorrect, as usb is not a valid filesystem type for mount. References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 14: Managing Disk Storage, page 455.
A systems administrator is compiling a report containing information about processes that are listening on the network ports of a Linux server. Which of the following commands will allow the administrator to obtain the needed information?
Correct Answer:
A
The command ss -pint will allow the administrator to obtain the needed information about processes that are listening on the network ports of a Linux server.
The ss command is a tool for displaying socket statistics on Linux systems. Sockets are endpoints of network communication that allow processes to exchange data over the network. The ss command can show various information about the sockets, such as the state, address, port, protocol, and process. The -pint option specifies the filters and flags that the ss command should apply. The -p option shows the process name and ID that owns the socket. The -i option shows the internal information about the socket, such as the send and receive queue, the congestion window, and the retransmission timeout. The -
n option shows the numerical address and port, instead of resolving the hostnames and service names. The -t option shows only the TCP sockets, which are the most common type of sockets used for network communication. The command ss -pint will display the socket statistics for the TCP sockets, along with the process name and ID, the numerical address and port, and the internal information. This will allow the administrator to obtain the needed information about processes that are listening on the network ports of a Linux server. This is the correct command to use to obtain the needed information. The other options are incorrect because they either do not show the socket statistics (tcpdump - nL or lsof -It) or do not show the process name and ID (netstat -pn). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 389.
A systems administrator received a notification that a system is performing slowly. When running the top command, the systems administrator can see the following values:
Which of the following commands will the administrator most likely run NEXT?
Correct Answer:
A
The command vmstat will most likely be run next by the administrator to troubleshoot the system performance. The vmstat command is a tool for reporting virtual memory statistics on Linux systems. The command shows information about processes, memory, paging, block IO, interrupts, and CPU activity. The command can help the administrator identify the source of the performance issue, such as high CPU usage, low free memory, excessive swapping, or disk IO bottlenecks. The command can also be used with an interval and a count to display the statistics repeatedly over time and observe the changes. The command vmstat will provide useful information for diagnosing the system performance and finding the root cause of the issue. This is the most likely command to run next after the top command. The other options are incorrect because they either do not show the virtual memory statistics (strace or lsof) or do not provide more information than the top command (htop). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 14: Managing Processes and Scheduling Tasks, page 425.

