Which of the following data structures is written in JSON?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Correct Answer:
C
Option C is the only data structure that is written in JSON format. JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation, and it is a lightweight and human-readable data interchange format. JSON uses curly braces to enclose objects, which consist of key-value pairs separated by commas. JSON uses square brackets to enclose arrays, which consist of values separated by commas. JSON supports six data types: strings, numbers, booleans, null, objects, and arrays. Option C follows these rules and syntax of JSON, while the other options do not. Option A is written in XML format, which uses tags to enclose elements and attributes. Option B is written in YAML format, which uses indentation and colons to define key-value pairs. Option D is written in INI format, which uses sections and equal signs to define key-value pairs. References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 21: Automating Tasks with Ansible, page 591.
A systems administrator is trying to track down a rogue process that has a TCP listener on a network interface for remote command-and-control instructions.
Which of the following commands should the systems administrator use to generate a list of rogue process names? (Select two).
Correct Answer:
AB
The best commands to use to generate a list of rogue process names that have a TCP listener on a network interface are A. netstat -antp | grep LISTEN and B. lsof -iTCP | grep LISTEN. These commands will show the process ID (PID) and name of the processes that are listening on TCP ports, which can be used to identify any suspicious or unauthorized processes. The other commands are either not specific enough, not valid, or not relevant for this task. For example:
✑ C. lsof -i:22 | grep TCP will only show the processes that are listening on port 22, which is typically used for SSH, and not any other ports.
✑ D. netstat -a | grep TCP will show all the TCP connections, both active and listening, but not the process names or IDs.
✑ E. nmap -p1-65535 | grep -i tcp will scan all the TCP ports on the local host, but not show the process names or IDs.
✑ F. nmap -sS 0.0.0.0/0 will perform a stealth scan on the entire internet, which is not only impractical, but also illegal in some countries.
A Linux user reported the following error after trying to connect to the system remotely: ssh: connect to host 10.0.1.10 port 22: Resource temporarily unavailable
The Linux systems administrator executed the following commands in the Linux system while trying to diagnose this issue: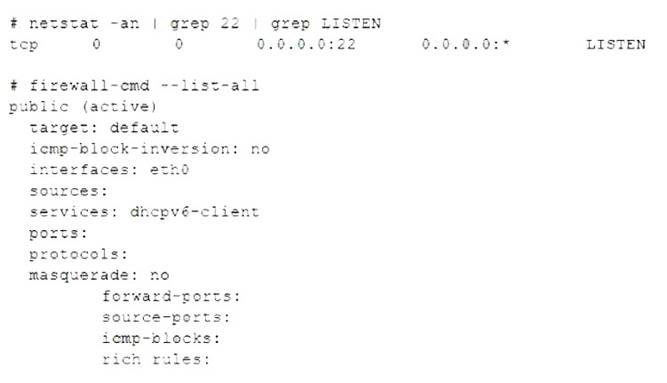
Which of the following commands will resolve this issue?
Correct Answer:
C
The firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=ssh command will resolve the issue by allowing SSH connections on port 22 in the public zone of the firewalld service. This command will add the ssh service to the permanent configuration of the public zone, which means it will persist after a reboot or a reload of the firewalld service. The firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=22 command is invalid, as 22 is not a valid service name. The systemct1 enable firewalld; systemct1 restart firewalld command will enable and restart the firewalld service, but it will not change the firewall rules. The firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=22/udp command will allow UDP traffic on port 22 in the public zone, but SSH uses TCP, not UDP. References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 18: Securing Linux Systems, page 543.
A Linux system fails to start and delivers the following error message:
Which of the following commands can be used to address this issue?
Correct Answer:
A
The command fsck.ext4 /dev/sda1 can be used to address the issue. The issue is caused by a corrupted filesystem on the /dev/sda1 partition. The error message shows that the filesystem type is ext4 and the superblock is invalid. The command fsck.ext4 is a tool for checking and repairing ext4 filesystems. The command will scan the partition for errors and attempt to fix them. This command can resolve the issue
and allow the system to start. The other options are incorrect because they either do not fix the filesystem (partprobe or fdisk) or destroy the data on the partition (mkfs.ext4). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 10: Managing Storage, page 325.
Due to low disk space, a Linux administrator finding and removing all log files that were modified more than 180 days ago. Which of the following commands will accomplish this task?
Correct Answer:
C
The command that will accomplish the task of finding and removing all log files that were modified more than 180 days ago is find /var/log -type f -mtime +180 -exec rm {} ;. This command will use find to search for files (-type f) under /var/log directory that have a modification time (-mtime) older than 180 days (+180). For each matching file, it will execute (-exec) the rm command to delete it, passing the file name as an argument ({}). The command will end with a semicolon (;), which is escaped with a backslash to prevent shell interpretation.
The other options are not correct commands for accomplishing the task. The find /var/log - type d -mtime +180 -print -exec rm {} ; command will search for directories (-type d) instead of files, and print their names (-print) before deleting them. This is not what the task requires. The find /var/log -type f -modified +180 -rm command is invalid because there is no such option as -modified or -rm for find. The correct options are -mtime and -delete, respectively. The find /var/log -type c -atime +180 –remove command is also invalid because there is no such option as –remove for find. Moreover, it will search for character special files (-type c) instead of regular files, and use access time (-atime) instead of modification time. References: find(1) - Linux manual page; Find and delete files older than n days in Linux

