In which of the following filesystems are system logs commonly stored?
Correct Answer:
A
The filesystem that system logs are commonly stored in is /var. The /var filesystem is a directory that contains variable data files on Linux systems. Variable data files are files that are expected to grow in size over time, such as logs, caches, spools, and temporary files. The /var filesystem is separate from the / filesystem, which contains the essential system files, to prevent the / filesystem from being filled up by the variable data files. The system logs are files that record the events and activities of the system and its components, such as the kernel, the services, the applications, and the users. The system logs are useful for monitoring, troubleshooting, and auditing the system. The system logs are commonly stored in the /var/log directory, which is a subdirectory of the /var filesystem. The /var/log directory contains various log files, such as syslog, messages, dmesg, auth.log, and kern.log. The filesystem that system logs are commonly stored in is /var. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they are not the filesystems that system logs are commonly stored in (/tmp, /etc, or /opt). References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 16: Managing Logging and Monitoring, page 487.
A user reported issues when trying to log in to a Linux server. The following outputs were received:
Given the outputs above. which of the following is the reason the user is una-ble to log in to the server?
Correct Answer:
D
The user1 password is expired. This can be inferred from the output of the chage -l user1 command, which shows the password expiration information for user1. The output shows that the password expired on 2020-10-01, and the account expired on 2020-10-08. This means that user1 cannot log in to the server unless the password and account are reactivated by the system administrator.
The other options are not correct based on the outputs above. User1 does not need to set a long password, because the output of the passwd -S user1 command shows that the password has a minimum length of 5 characters, which is met by user1’s password. User1 is not in the incorrect group, because the output of the groups user1 command shows that user1 belongs to the app group, which is presumably the correct group for accessing the server. The user1 shell assignment is not incorrect, because the output of the grep user1
/etc/passwd command shows that user1 has /bin/bash as the default shell, which is a valid and common shell for Linux users.
DRAG DROP
As a Systems Administrator, to reduce disk space, you were tasked to create a shell script that does the following:
Add relevant content to /tmp/script.sh, so that it finds and compresses rotated files in
/var/log without recursion. INSTRUCTIONS
Fill the blanks to build a script that performs the actual compression of rotated log files.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.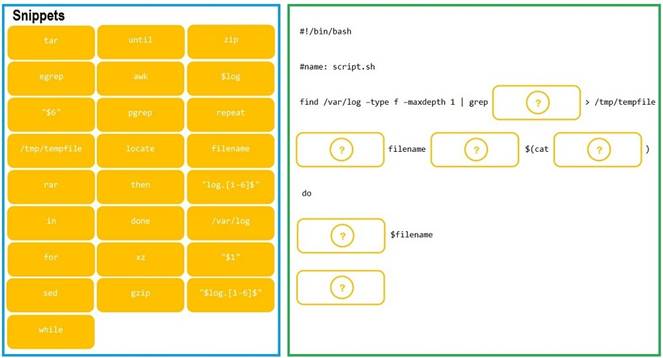
Solution: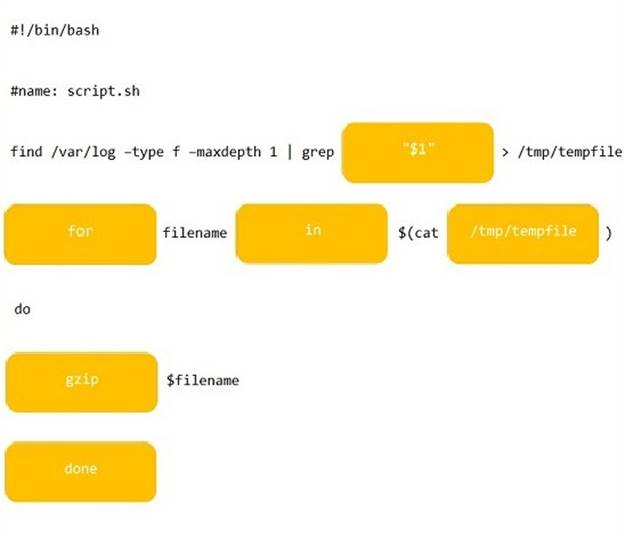
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:
A
Which of the following technologies can be used as a central repository of Linux users and groups?
Correct Answer:
A
LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, which is a protocol for accessing and managing a central directory of users and groups. LDAP can be used as a central repository of Linux users and groups, allowing for centralized authentication and authorization across multiple Linux systems. MFA, SSO, and PAM are not technologies that can be used as a central repository of Linux users and groups. MFA stands for Multi- Factor Authentication, which is a method of verifying a user’s identity using more than one factor, such as a password, a token, or a biometric. SSO stands for Single Sign-On, which is a feature that allows a user to log in once and access multiple applications or systems without having to re-enter credentials. PAM stands for Pluggable Authentication Modules, which is a framework that allows Linux to use different authentication methods, such as passwords, tokens, or biometrics. References: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 8: Managing Users and Groups
A Linux administrator is configuring a new internal web server fleet. The web servers are up and running but can only be reached by users directly via IP address. The administrator is attempting to fix this inconvenience by requesting appropriate records from the DNS team. The details are:
Hostname: devel.comptia.org
IP address: 5.5.5.1, 5.5.5.2, 5.5.5.3, 5.5.5.4
Name server: 5.5.5.254
Additional names: dev.comptia.org, development.comptia.org
Which of the following types of DNS records should the Linux administrator request from the DNS team? (Select three).
Correct Answer:
BDE
The Linux administrator should request the following types of DNS records from the DNS team:
✑ A: This record type is used to map a hostname to an IPv4 address. The administrator needs four A records for devel.comptia.org, one for each IP address (5.5.5.1, 5.5.5.2, 5.5.5.3, 5.5.5.4). This will allow users to access the web servers by using the hostname devel.comptia.org instead of the IP addresses1.
✑ CNAME: This record type is used to create an alias for another hostname. The administrator needs two CNAME records, one for dev.comptia.org and one for development.comptia.org, both pointing to devel.comptia.org. This will allow users to access the web servers by using any of these three hostnames interchangeably1.
✑ NS: This record type is used to delegate a domain or a subdomain to another name server. The administrator needs one NS record for comptia.org, pointing to 5.5.5.254, which is the name server that hosts the records for the subdomain devel.comptia.org2. This will allow users to resolve the hostnames under comptia.org by querying the name server 5.5.5.2542.
The other record types are not relevant for the administrator’s task:
✑ MX: This record type is used to specify the mail exchange server for a domain or a subdomain1. The administrator does not need this record type because the web servers are not intended to handle email traffic.
✑ PTR: This record type is used to map an IP address to a hostname, which is the reverse of an A record1. The administrator does not need this record type because the web servers are not expected to be accessed by their IP addresses.
✑ RRSIG: This record type is used to provide digital signatures for DNSSEC, which is a security extension for DNS that verifies the authenticity and integrity of DNS responses3. The administrator does not need this record type because it is not mentioned in the task requirements.
✑ SOA: This record type is used to provide information about the authoritative name server and other parameters for a domain or a subdomain1. The administrator does not need this record type because it is usually created automatically by the name server software when a new zone file is created4.
✑ TXT: This record type is used to store arbitrary text data that can be used for various purposes, such as SPF, DKIM, DMARC, etc1. The administrator does not need this record type because it is not related to the web server functionality.
✑ SRV: This record type is used to specify the location and port number of a service that runs on a domain or a subdomain1. The administrator does not need this record type because the web servers use the standard HTTP port 80, which does not require an SRV record.
References: 1: DNS Record Types – CompTIA Network+ N10-007 – 1.8 2: NS Record - DNSimple Help 3: DNSSEC - Wikipedia 4: SOA Record - DNSimple Help

