Andy is the project manager of the NHGQ project for his organization. He has elected to use a three-point estimate for his project. His project team, however, is complaining about participating in this estimate type because of the time it takes to predict the duration of activities. Andy, as the project manager, tells the project team that they must create the time estimate, as it will help this project and future similar projects. What is a three-point estimate?
Correct Answer:
B
A three-point estimate requires that each activity be estimated for its optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic duration. Once the three estimates have been created, an average of the duration estimates is found and this is the recorded duration for the project work.
Answer option A is incorrect. This is not a complete explanation of a three-point estimate. Answer option C is incorrect. This is a definition of PERT, a similar time estimating technique.
Answer option D is incorrect. This is definition of PERT, but this answer uses the term GERT so it is not a valid choice.
You are the project manager for your organization. Your project is doing fine on time and cost, but management wants to address the project performance for future accomplishment. Management has asked you to begin reporting and forecasting your project's health based on a moving average, extrapolation, trend estimation, and growth curve. What type of forecasting method is management asking you to use?
Correct Answer:
C
These are examples of a time series method for forecasting project performance. Another method that fits with the time series method of forecasting is earned value management. Forecasting is the process of estimating or predicting in unknown situations. Forecasting is about predicting the future as accurately as possible with the help of all the information available, including historical data and knowledge of any future events that might impact forecasts. The forecasting methods are categorized as follows: Time series method: It uses historical data as the basis for estimating future outcomes. Causal/econometric method: This forecasting method is based on the assumption that it is possible to identify some factors that might influence the variable that is being forecasted. If the causes are understood, projections of the influencing variables can be made and used in the forecast. Judgmental method: Judgmental forecasting methods incorporate intuitive judgments, opinions, and subjective probability estimates. Other methods: Other methods may include probabilistic forecasting, simulation, and ensemble forecasting.
Answer option B is incorrect. Causal/econometric methods do not use the moving average, but models such as linear regression and non- linear regression.
Answer option A is incorrect. Judgmental methods for forecasting are based on intuition, opinions, and probability estimates.
Answer option D is incorrect. The estimate at completion method is an earned value management formula, which is part of the time series method for reporting and forecasting performance.
You are the project manager of the GUH project. You are using the critical chain scheduling method as your approach to project scheduling. What two items can you compare in the critical chain method to determine if corrective action is appropriate?
Correct Answer:
D
The difference between the buffer needed and the buffer remaining can determine whether corrective action is appropriate.
Answer option C is incorrect. This is not an accurate description of how the critical chain determines the need for corrective action.
Answer option B is incorrect. This is not an accurate description of how the critical chain determines the need for corrective action.
Answer option A is incorrect. This is not an accurate description of how the critical chain determines the need for corrective action.
Gary is the project manager for his organization. At each weekly status meeting with his project team, Gary collects information on the work that has been completed and reviews the work that is remaining in the project. Alice, one of Gary's project team members, consistently reports that she's late on her project work. After the meeting, Gary and Alice discuss why the work is late as it is causing other delays in the project. What is the review of the late work commonly called?
Correct Answer:
A
Variance analysis is the study to determine why a variance in the project exists. Alice's late work may be for a number of reasons so Gary needs to determine why in order to address the problem. Variance analysis is a process that examines the dissimilarities between the planned and the actual budget or schedule in order to discover unacceptable risks to the budget, schedule, quality, or scope of the project. It is a method for resolving the total variance in the set of scope, schedule, and cost variables into particular component variances that are associated with defined factors affecting the cost, scope and schedule variables.
Answer option D is incorrect. Discipline is not the best answer as Gary, at this point, is simply reviewing the situation to determine why the variance exists.
Answer option C is incorrect. Quality control is the inspection of the work results to prove the existence of quality and to prevent mistakes from reaching the customer.
Answer option B is incorrect. This may be a type of leadership, but it is not the best answer for the question.
You are the project manager of the GHQ Project. You have to prioritize activities for the effective management of project. For this, you have created a network diagram to schedule a set of project activities as shown in the figure: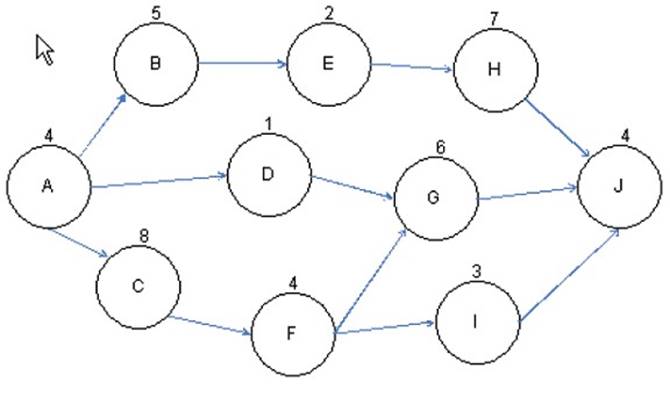
Based on this figure, what is the critical path of this project?
Correct Answer:
D
The activity nodes of path ACFGJ equals 26 days and is the longest path to completion - it is the critical path.
ACFGJ= A(4)+C(8)+F(4)+G(6)+J(4)=26
What is a critical path?
A critical path is the sequence of project activities, which add up to the longest overall duration. This determines the shortest time possible to complete the project. Any delay of an activity on the critical path directly impacts the planned project completion date (i.e. there is no float on the critical path). A project can have several, parallel, near critical paths. An additional parallel path through the network with the total durations shorter than the critical path is called a sub-critical or non-critical path. These results allow managers to prioritize activities for the effective management of project completion, and to shorten the planned critical path of a project by pruning critical path activities, by "fast tracking" (i.e., performing more activities in parallel), and/or by "crashing the critical path" (i.e., shortening the durations of critical path activities by adding resources).
Answer option A is incorrect. ABEHJ takes only 22 days to complete; it is not the critical path. ABEHJ=A(4)+B(5)+E(2)+H(7)+J(4)=22
Answer option C is incorrect. ADGJ takes only 15 days to complete; it is not the critical path. ADGJ=A(4)+D(1)+G(6)+J(4)=15
Answer option B is incorrect. ACFIJ takes only 23 days to complete; it is not the critical path. ACFIJ=A(4)+C(8)+F(4)+I(3)+J(4)=23

