An engineer is reviewing the following high availability (HA) settings to understand a recent HAfailover event.
Which timer determines the frequency between packets sent to verify that the HA functionality on the other HA firewall is operational?
Correct Answer:
D
The timer that determines the frequency between packets sent to verify that the HA functionality on the other HA firewall is operational is the Hello Interval. The Hello Interval is the interval in milliseconds between hello packets that are sent to check the HA status of the peer firewall. The default value for the Hello Interval is 8000 ms for all platforms, and the range is 8000-60000 ms. If the firewall does not receive a hello packet from its peer within the specified interval, it will declare the peer as failed and initiate a failover12. References: H Timers, Layer 3 High Availability with Optimal Failover Times Best Practices
How to Configure Ping Interval/Timeout Settings ... - Palo Alto Networks
Which log type would provide information about traffic blocked by a Zone Protection profile?
Correct Answer:
D
https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000ClhzCAC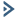 D is the correct answer because the threat log type would provide information about traffic blocked by a Zone Protection profile. This is because Zone Protection profiles are used to protect the network from attacks, including common flood, reconnaissance attacks, and other packet-based attacks1. These attacks are classified as threats by the firewall and are logged in the threat log2. The threat log displays information such as the source and destination IP addresses, ports, zones, applications, threat types, actions, and severity of the threats2.
D is the correct answer because the threat log type would provide information about traffic blocked by a Zone Protection profile. This is because Zone Protection profiles are used to protect the network from attacks, including common flood, reconnaissance attacks, and other packet-based attacks1. These attacks are classified as threats by the firewall and are logged in the threat log2. The threat log displays information such as the source and destination IP addresses, ports, zones, applications, threat types, actions, and severity of the threats2.
Verified References: 1: Zone protection profiles - Palo Alto Networks Knowledge Base
1: Zone protection profiles - Palo Alto Networks Knowledge Base  2: Threat Log Fields - Palo Alto Networks
2: Threat Log Fields - Palo Alto Networks
In the New App Viewer under Policy Optimizer, what does the compare option for a specific rule allow an administrator to compare?
Correct Answer:
B
The compare option for a specific rule in the New App Viewer under Policy Optimizer allows an administrator to compare the applications configured in the rule with the applications seen from traffic matching the same rule. This helps the administrator to identify any new applications that are not explicitly defined in the rule, but are implicitly allowed by the firewall based on the dependencies of the configured applications. The compare option also shows the usage statistics and risk levels of the applications, and provides suggestions for optimizing the rule by adding, removing, or replacing applications12. References: New App Viewer (Policy Optimizer), PCNSE Study Guide (page 47)
Why use Security Policy Optimizer and what are the benefits?
With the default TCP and UDP settings on the firewall, what will be the identified application in the following session?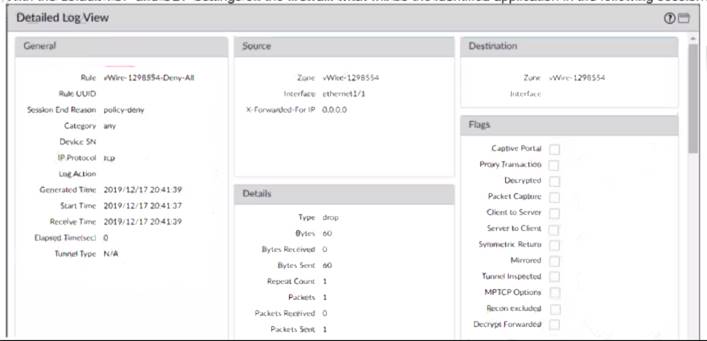
Correct Answer:
D
Traffic didnt match any other policies and so landed at the implicit "deny all" policy. If it's deny all, the traffic was dropped before the application could be determined. https://knowledgebase.paloaltonetworks.com/KCSArticleDetail?id=kA10g000000ClibCAC
A firewall engineer creates a NAT rule to translate IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10. The engineer also plans to enable DNS rewrite so that the firewall rewrites the IPv4 address in a DNS response based on the original destination IP address and translated destination IP address configured for the rule. The engineer wants the firewall to rewrite a DNS response of 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10.
What should the engineer do to complete the configuration?
Correct Answer:
B
If the DNS response matches the Original Destination Address in the rule, translate the DNS response using the same translation the rule uses. For example, if the rule translates IP address 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10, the firewall rewrites a DNS response of 1.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.10.
https://docs.paloaltonetworks.com/pan-os/9-1/pan-os-admin/networking/nat/source-nat-and-destination-nat/desti

