In which phase of the ADM cycle do building blocks become implementation-specific?
Correct Answer:
D
Building blocks are reusable components of business, IT, or architectural capability that can be combined to deliver architectures and solutions. Building blocks can be defined at various levels of detail, depending on the stage of architecture development. In the earlier phases of the ADM cycle (A to D), building blocks are defined in generic terms, such as logical or physical, to provide a high-level view of the architecture. In Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions, building blocks become implementation-specific, meaning that they are linked to specific products, standards, technologies, and vendors that are available in the market. This phase also identifiesthe delivery vehicles, such as projects, programs, or portfolios, that will realize the building blocks12 References: 1: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2, Part II: Architecture Development Method (ADM), Chapter 23:
Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions 2: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2, Part IV: Architecture Content Framework, Chapter 36: Building Blocks
Complete the sentence. The key purpose of Gap Analysis is to
Correct Answer:
B
Gap Analysis is a technique that compares the Baseline Architecture and the Target Architecture to identify the differences and gaps between them. The purpose of this technique is to determine the changes and additions that are required to achieve the desired future state of the architecture. One of the main aspects of Gap Analysis is to identify the functions that aremissing or overlapping in the current and future architectures, and to plan how to address them. This helps to ensure that the architecture is complete, consistent, and aligned with the business objectives and requirements3
Which of the following best describes the purpose of the Gap Analysis technique?
Correct Answer:
C
The purpose of the Gap Analysis technique is similar to the previous question, but with a focus on the Target Architecture. The technique helps to identify the items that are not included or specified in the Target Architecture, such as capabilities, services, components, standards, or technologies. These items may be essential for achieving the vision and goals of the enterprise, or for addressing the stakeholder concerns and requirements. By identifying the items omitted from the Target Architecture, the technique helps to ensure that the architecture is comprehensive, feasible, and realistic.
What does the TOGAF ADM recommend for use in developing an Architecture Vision document?
Correct Answer:
D
Business scenarios are a technique recommended by the TOGAF ADM for use in developing an Architecture Vision document12. Business scenarios are a means of capturing the business requirements and drivers, the processes and actors involved, and the desired outcomes and measures of success34.Business scenarios help to create a common vision and understanding among the stakeholders, and to identify and validate the architecture requirements . Business scenarios also provide a basis for analyzing the impact and value of the proposed architecture. References:
•The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Phase A: Architecture Vision - The Open Group
•TOGAF® Standard — Introduction - Phase A: Architecture Vision
•The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Definitions - The Open Group
•Business Scenarios - The Open Group
•[The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Architecture Requirements Specification - The Open Group]
•[The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Architecture Vision - The Open Group]
•[The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Business Transformation Readiness Assessment - The Open Group]
Exhibit: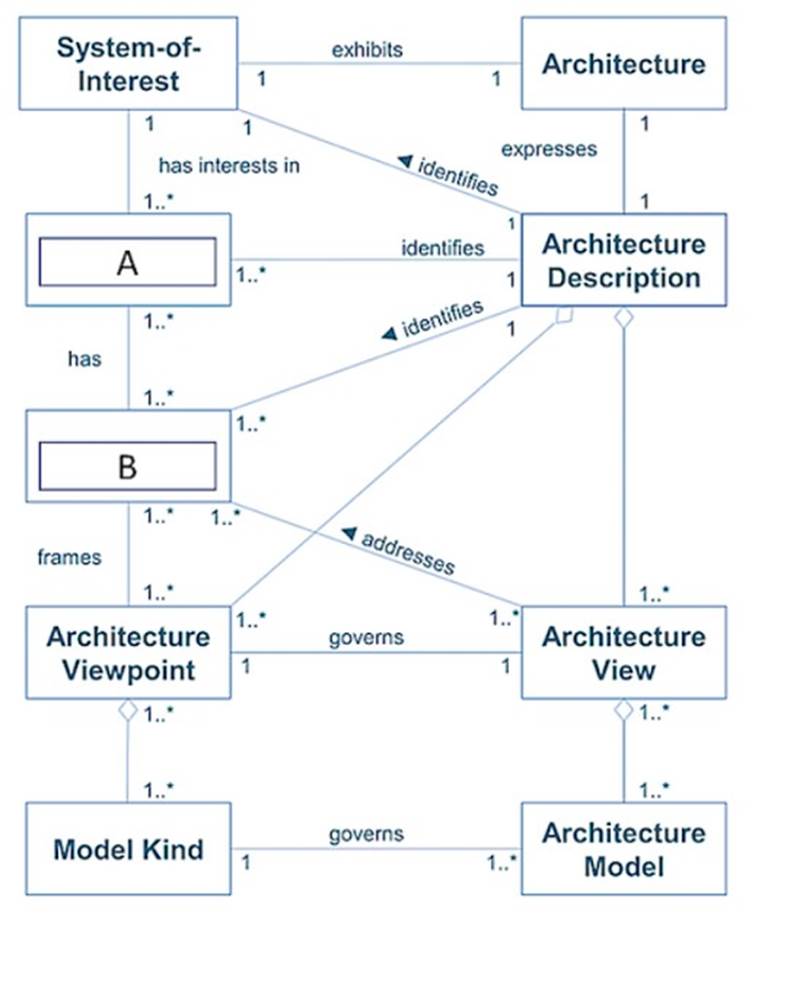
Consider the image showing basic architectural concepts. What are items A and B?
Correct Answer:
C
In the context of TOGAF, a stakeholder is any individual, team, or
organization who has interests in, or concerns relative to, the outcome of the architecture. Concerns are those interests which pertain to any aspect of the system??s functioning, development or operation, including considerations such as performance, reliability, and security1. References:
•The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Definitions - The Open Group

