Refer to the exhibit.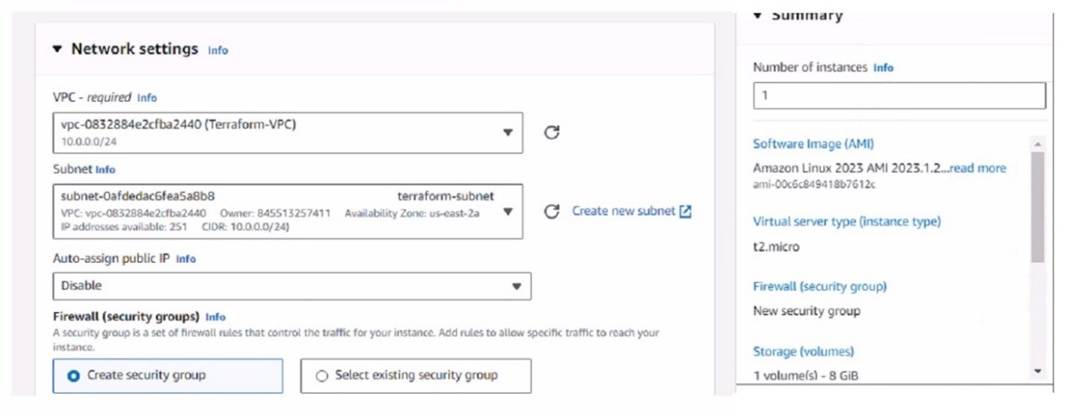
You have deployed a Linux EC2 instance in Amazon Web Services (AWS) with the settings shown on the exhibit
What next step must the administrator take to access this instance from the internet?
Correct Answer:
D
The next step the administrator must take to access the Linux EC2 instance from the internet is:
D.Allocate an Elastic IP address and assign it to the instance.
✑ Elastic IP (EIP) Requirement:By default, when an EC2 instance is launched in AWS, it receives a public IP address from Amazon's pool, which is not static. This IP address can change, for example, if the instance is stopped and started again. To have a static IP address, you need to allocate an Elastic IP (EIP), which is a persistent public IP address, and then associate it with the instance.
✑ Public Accessibility:Without an Elastic IP, the instance may not be accessible over the internet after a reboot or stop/start sequence. Assigning an Elastic IP ensures the instance can be accessed consistently using the same IP address.
References:The AWS documentation on EC2 instances details the process and need for Elastic IPs to ensure consistent internet access to instances.
Refer to Exhibit: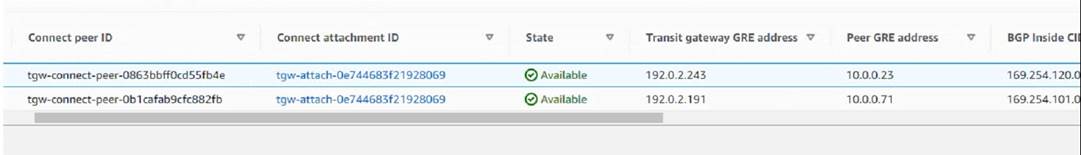
The exhibit shows the Connect Peers settings on Amazon Web Services (AWS) transit gateway attachments With two FortiGate VMS in a security VPC.
Which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AB
* A. The peer GRE address is the FortiGate external interface IP address. This is the IP address of the FortiGate interface that is connected to the transit gateway attachment subnet1. This IP address is used to establish the GRE tunnel between the FortiGate and the transit gateway2. B. The Transit Gateway GRE address is auto-generated. This is the IP address of the transit gateway that is used to establish the GRE tunnel with the FortiGate2. This IP address is automatically assigned by AWS from the Transit Gateway CIDR range that you specify when you create the Connect attachment3.
The other options are incorrect because:
✑ The BGP inside CIDR blocks cannot be any CIDR block with /29. They must be a /29 CIDR block from the 169.254.0.0/16 range for IPv4, or a /125 CIDR block from the fd00::/8 range for IPv64. These are the inside IP addresses that are used for BGP peering over the GRE tunnel4.
✑ The Peer GRE address is not the FortiGate internal interface IP address. The internal interface IP address is used to route traffic from the FortiGate to the VPC subnet where the third-party appliance (such as SD-WAN) is located1. The Peer GRE address is used to route traffic from the FortiGate to the transit gateway over the GRE tunnel2.
You are configuring the failover settings on a FortiGate active-passive SDN connector solution in Microsoft Azure. Which two mandatory settings are required after the initial deployment? (Choose two)
Correct Answer:
AD
For configuring the failover settings on a FortiGate active-passive SDN connector solution in Microsoft Azure, the two mandatory settings required after the initial deployment are: A.Subscription-id D.Resource group name
✑ Subscription ID:This is a unique identifier for your Azure subscription under which all resources are created and billed. FortiGate needs this to interact with the Azure resources associated with that subscription.
✑ Resource Group Name:A resource group in Azure is a container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. The SDN connector requires the resource group name to correctly identify and manage the resources it should control, especially in a failover scenario.
References:The requirement for these specific details is found in Azure's best practices for resource management and Fortinet's documentation on deploying and configuring FortiGate appliances in Azure environments.
Refer to Exhibit:
You are troubleshooting a Microsoft Azure SDN connector issue on your FortiGate VM in Azure
Which three settings should you check while troubleshooting this problem? (Choose three.)
Correct Answer:
CDE
The three settings that should be checked while troubleshooting this problem are:
✑ Ensure FortiGate port4 can resolve DNS. This is because the Azure SDN connector requires DNS resolution to communicate with the Azure API1. If the FortiGate port4 cannot resolve DNS, the SDN connector will not be able to retrieve the Azure resources and display them in the GUI.
✑ Ensure FortiGate portl has internet access. This is because the Azure SDN connector requires internet access to communicate with the Azure API1. If the FortiGate portl does not have internet access, the SDNconnector will not be able to connect to the Azure cloud and display an error in the CLI.
✑ Ensure IP address 169.254.169_254 is not blocked. This is because the Azure SDN connector uses this IP address to obtain metadata information from the Azure instance2. If this IP address is blocked by a firewall policy or a network ACL, the SDN connector will not be able to get the required information and display an error in the CLI.
How does an administrator secure container environments from newly emerged security threats?
Correct Answer:
D
Securing container environments from newly emerged security threats involves employing specific security mechanisms tailored to the technology and structure of containers. In this context, the use of Docker-related application control signatures (Option D) is critical for effectively managing and mitigating threats in containerized environments.
✑ Docker-Specific Threats:Docker containers, being a prevalent form of container technology, are targeted by various security threats, including those that exploit vulnerabilities specific to the Docker environment and runtime. Using Docker- related application control signatures means implementing security measures that are specifically designed to detect and respond to anomalies and threats that are unique to Docker containers.
✑ Application Control Signatures:These are sets of definitions that help identify and block potentially malicious activities within application traffic. By focusing on Docker-related signatures, administrators can ensure that the security tools are finely tuned to the operational specifics of Docker containers, thereby providing a robust defense against exploits that target container-specific vulnerabilities.
References:The recommendation to use Docker-related application control signatures is based on best practices for securing container environments, emphasizing the need for specialized security measures that address the unique challenges posed by container technologies.

