Refer to the exhibit.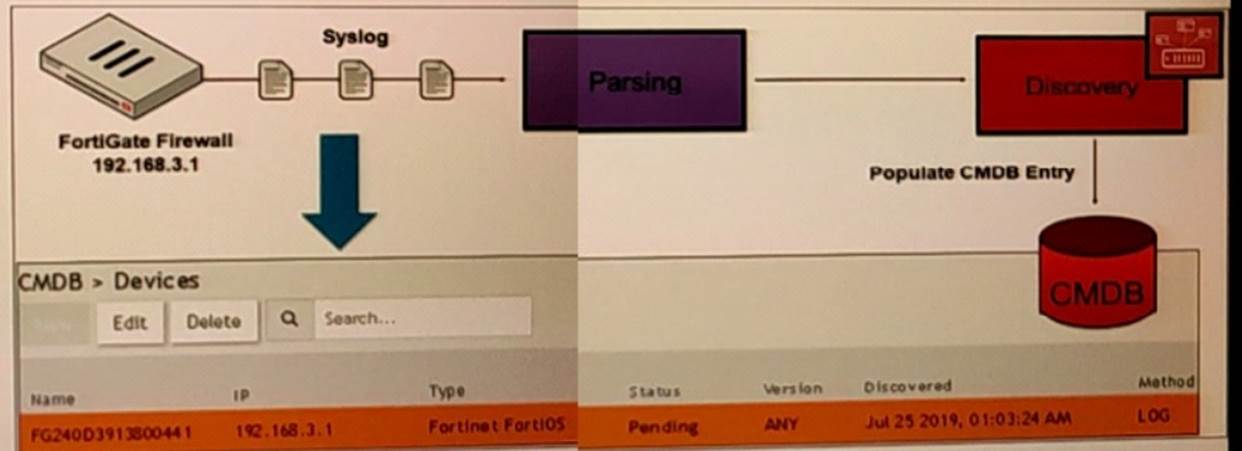
How was the FortiGate device discovered by FortiSIEM?
Correct Answer:
B
Discovery Methods in FortiSIEM: FortiSIEM can discover devices using various methods, including syslog, SNMP, and others. Syslog Discovery: The exhibit shows that the FortiGate device is discovered by FortiSIEM using syslog.
Syslog Parsing: The syslog messages sent by the FortiGate device are parsed by FortiSIEM to extract relevant information.
CMDB Entry: Based on the parsed information, an entry is populated in the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) for the device.
Evidence in Exhibit: The exhibit shows the syslog flow from the FortiGate Firewall to the parsing and discovery process, resulting in the device being listed in the CMDB with the status 'Pending.'
References: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Device Discovery section, which explains how syslog discovery works and how devices are added to the CMDB based on syslog data.
Refer to the exhibit.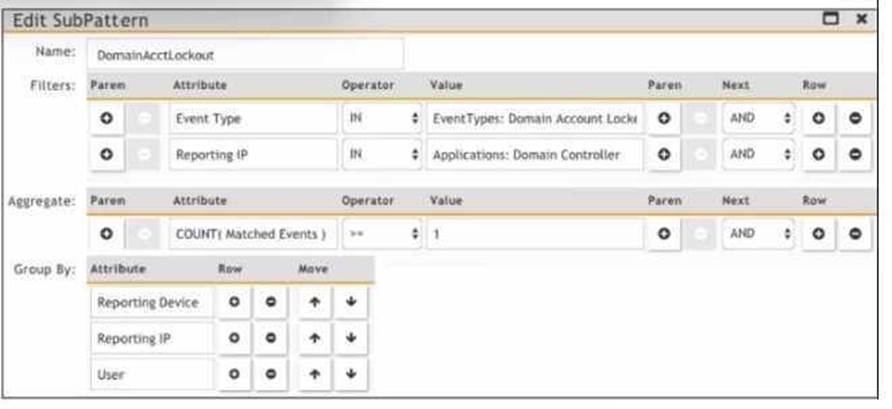
Which section contains the sortings that determine how many incidents are created?
Correct Answer:
B
Incident Creation in FortiSIEM: Incidents in FortiSIEM are created based on specific patterns and conditions defined within the system.
Group By Function: The "Group By" section in the "Edit SubPattern" window specifies how the data should be grouped for analysis and incident creation.
Impact of Grouping: The way data is grouped affects the number of incidents generated.
Each unique combination of the grouped attributes results in a separate incident.
Exhibit Analysis: In the provided exhibit, the "Group By" section lists "Reporting Device," "Reporting IP," and "User." This means incidents will be created for each unique combination of these attributes. References: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Rule and Pattern Creation section, which details how grouping impacts incident generation.
When configuring collectors located in geographically separated sites, what ports must be open on
a front end firewall?
Correct Answer:
B
FortiSIEM Architecture: In FortiSIEM, collectors gather data from various sources and send this
data to supervisors and workers within the FortiSIEM architecture.
Communication Requirements: For collectors to effectively send data to the FortiSIEM system, specific communication channels must be open.
Port Usage: The primary port used for secure communication between the collectors and the FortiSIEM infrastructure is HTTPS (port 443).
Network Configuration: When configuring collectors in geographically separated sites, the HTTPS port must be open for the collectors to communicate with both the supervisor and the worker upload settings addresses. This ensures that the collected data can be securely transmitted to the appropriate processing and analysis components.
References: FortiSIEM 6.3 Administration Guide, Network Ports section details the necessary ports for communication within the FortiSIEM architecture.
Which command displays the Linux agent status?
Correct Answer:
C
Explanation
Linux Agent in FortiSIEM: The FortiSIEM Linux agent is responsible for collecting logs and metrics from Linux devices and forwarding them to the FortiSIEM system.
Command for Checking Status: The correct command to check the status of the FortiSIEM Linux agent isservice fortisiem-linux-agent status.
This command queries the status of the FortiSIEM Linux agent service, showing whether it is running, stopped, or encountering issues.
Usage: Properly checking the agent status helps ensure that data collection from Linux devices is functioning as expected.
References: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Linux Agent Installation and Management section, which includes commands for managing the Linux agent.
Device discovery information is stored in which database?
Correct Answer:
A

