An organization has created an API-led architecture that uses various API layers to integrate mobile clients with a backend system. The backend system consists of a number of specialized components and can be accessed via a REST API. The process and experience APIs share the same bounded-context model that is different from the backend data model. What additional canonical models, bounded-context models, or anti-corruption layers are best added to this architecture to help process data consumed from the backend system?
Correct Answer:
C
Correct Answer:: Create a bounded-context model for the system layer to closely match the backend data model, and add an anti-corruption layer to let the different bounded contexts cooperate across the system and process layers
*****************************************
>> Canonical models are not an option here as the organization has already put in efforts and created bounded-context models for Experience and Process APIs.
>> Anti-corruption layers for ALL APIs is unnecessary and invalid because it is mentioned that experience and process APIs share same bounded-context model. It is just the System layer APIs that need to choose their approach now.
>> So, having an anti-corruption layer just between the process and system layers will work well. Also to speed up the approach, system APIs can mimic the backend system data model.
A system API is deployed to a primary environment as well as to a disaster recovery (DR) environment, with different DNS names in each environment. A process API is a client to the system API and is being rate limited by the system API, with different limits in each of the environments. The system API's DR environment provides only 20% of the rate limiting offered by the primary environment. What is the best API fault-tolerant invocation strategy to reduce overall errors in the process API, given these conditions and constraints?
Correct Answer:
A
Correct Answer:: Invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment; add timeout and retry logic to the process API to avoid intermittent failures; if it still fails, invoke the system API deployed to the DR environment
*****************************************
There is one important consideration to be noted in the question which is - System API in DR environment provides only 20% of the rate limiting offered by the primary environment. So, comparitively, very less calls will be allowed into the DR environment API opposed to its primary environment. With this in mind, lets analyse what is the right and best fault-tolerant invocation strategy.
* 1. Invoking both the system APIs in parallel is definitely NOT a feasible approach because of the 20% limitation we have on DR environment. Calling in parallel every time would easily and quickly exhaust the rate limits on DR environment and may not give chance to genuine intermittent error scenarios to let in during the time of need.
* 2. Another option given is suggesting to add timeout and retry logic to process API while invoking primary environment's system API. This is good so far. However, when all retries failed, the option is suggesting to invoke the copy of process API on DR environment which is not right or recommended. Only system API is
the one to be considered for fallback and not the whole process API. Process APIs usually have lot of heavy orchestration calling many other APIs which we do not want to repeat again by calling DR's process API. So this option is NOT right.
* 3. One more option given is suggesting to add the retry (no timeout) logic to process API to directly retry on DR environment's system API instead of retrying the primary environment system API first. This is not at all a proper fallback. A proper fallback should occur only after all retries are performed and exhausted on Primary environment first. But here, the option is suggesting to directly retry fallback API on first failure itself without trying main API. So, this option is NOT right too.
This leaves us one option which is right and best fit.
- Invoke the system API deployed to the primary environment
- Add Timeout and Retry logic on it in process API
- If it fails even after all retries, then invoke the system API deployed to the DR environment.
Refer to the exhibit.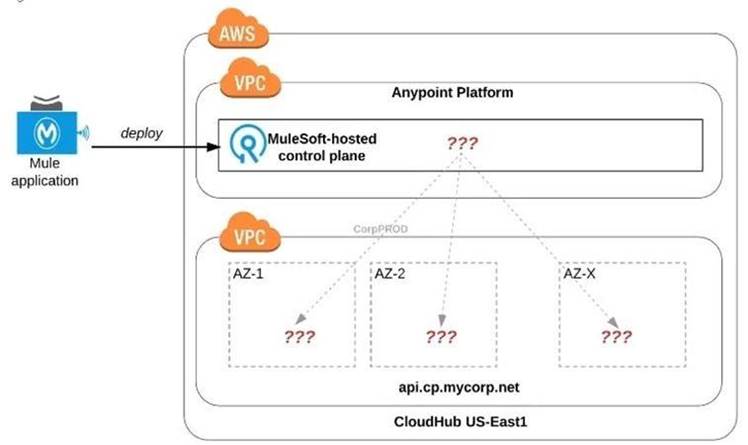
An organization uses one specific CloudHub (AWS) region for all CloudHub deployments.
How are CloudHub workers assigned to availability zones (AZs) when the organization's Mule applications are deployed to CloudHub in that region?
Correct Answer:
D
Correct Answer:: Workers are randomly distributed across available AZs within that region.
*****************************************
>> Currently, we only have control to choose which AWS Region to choose but there is no control at all using any configurations or deployment options to decide what Availability Zone (AZ) to assign to what worker.
>> There arNe O
fixed or implicit rules on platform too w.r.t assignment of AZ to workers based on
environment or application.
>> They are completely assigned inrandom. However, cloudhub definitely ensures that HA is achieved by assigning the workers to more than on AZ so that all workers are not assigned to same AZ for same application.
What Anypoint Connectors support transactions?
Correct Answer:
A

