Exhibit: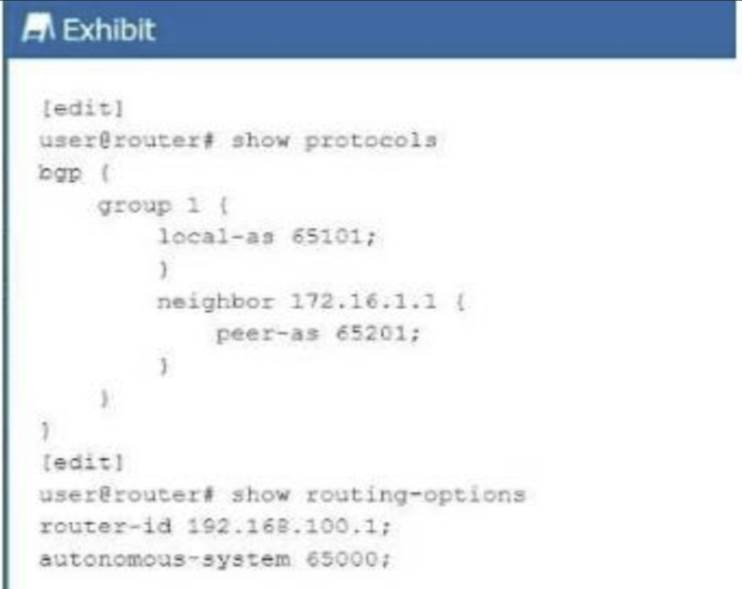
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
Correct Answer:
B
In the exhibit, BGP is configured withlocal AS 65101and a neighbor at172.16.1.1inpeer AS 65201. This setup involves two different Autonomous Systems (AS), indicating anExternal BGP (EBGP)configuration.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:  EBGP vs. IBGP:
EBGP vs. IBGP: EBGPis used between routers in different ASes. In this case, the local AS is65101and the peer AS is65201, meaning the BGP session isEBGP.
EBGPis used between routers in different ASes. In this case, the local AS is65101and the peer AS is65201, meaning the BGP session isEBGP. IBGPis used between routers within the same AS, which is not applicable here as the AS numbers are different.
IBGPis used between routers within the same AS, which is not applicable here as the AS numbers are different. BGP Group Configuration:
BGP Group Configuration: The configuration does not require a type external parameter because Junos OSautomatically recognizes the session asEBGPwhen the local and peer AS numbers are different.
The configuration does not require a type external parameter because Junos OSautomatically recognizes the session asEBGPwhen the local and peer AS numbers are different. The BGP session will operate as EBGP, and the configuration will commit successfully.
The BGP session will operate as EBGP, and the configuration will commit successfully.
Juniper Reference: BGP Configuration: In Juniper, EBGP is automatically recognized when the local and peer AS numbers differ, without needing to specify type external.
BGP Configuration: In Juniper, EBGP is automatically recognized when the local and peer AS numbers differ, without needing to specify type external.
What are two consequences of having all network devices in a single collision domain? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
CD
Acollision domainis a network segment where data packets can "collide" with one another when being sent on the same network medium.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Increased Collision Probability:If all devices are in asingle collision domain, the likelihood of packet collisions increases as more devices attempt to send packets simultaneously, leading to network inefficiencies.
Increased Resource Consumption:More collisions result inincreased network resource consumptionas devices need to retransmit packets, causing higher utilization of bandwidth and slowing down network performance.
Juniper Reference:
Collision Domains: Proper network segmentation using switches reduces collision domains, thereby improving network performance and reducing packet collisions.
Which statement is correct about aggregate routes?
Correct Answer:
D
An aggregate route is a summarized route that is created by combining multiple specific routes into a single, broader route. In Junos OS, when an aggregate route is configured, its default next hop is set toreject.
Step-by-Step Explanation:: Aggregate Route:Aggregate routes are used to reduce the size of routing tables by representing a collection of more specific routes with a single summary route. They help improve routing efficiency and scalability, especially in large networks.
Aggregate Route:Aggregate routes are used to reduce the size of routing tables by representing a collection of more specific routes with a single summary route. They help improve routing efficiency and scalability, especially in large networks. Default Next Hop Behavior:
Default Next Hop Behavior: When you configure an aggregate route in Junos OS, it has arejectnext hop by default.
When you configure an aggregate route in Junos OS, it has arejectnext hop by default. Therejectnext hop means that if a packet matches the aggregate route but there is no more specific route in the routing table for that destination, the packet will be discarded, and an ICMP "destination unreachable" message is sent to the source.
Therejectnext hop means that if a packet matches the aggregate route but there is no more specific route in the routing table for that destination, the packet will be discarded, and an ICMP "destination unreachable" message is sent to the source. This behavior helps to prevent routing loops and ensures that traffic isn't forwarded to destinations for which there is no valid route.
This behavior helps to prevent routing loops and ensures that traffic isn't forwarded to destinations for which there is no valid route. Modifying Next Hop:If needed, the next hop behavior of an aggregate route can be changed todiscard (which silently drops the packet) or to another specific next hop. However, by default, the next hop is set toreject.
Modifying Next Hop:If needed, the next hop behavior of an aggregate route can be changed todiscard (which silently drops the packet) or to another specific next hop. However, by default, the next hop is set toreject.
Juniper Reference: Junos Command: set routing-options aggregate route
Junos Command: set routing-options aggregate route  Verification: Use show route to verify the presence and behavior of aggregate routes.
Verification: Use show route to verify the presence and behavior of aggregate routes.
What is the main purpose of Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)?
Correct Answer:
A
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)is a network protocol used to detect failures in the network path
between two devices quickly.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Path Failure Detection:BFD provides a low-overhead mechanism for detecting failures in forwarding
paths across Layer 3 networks. It is much faster than traditional routing protocol timers and can detect
failures within milliseconds.
BFD in Routing:BFD can be integrated with routing protocols like OSPF, BGP, or IS-IS to trigger a
faster convergence when a network path goes down.
Juniper Reference:
BFD Configuration: Juniper devices use BFD to monitor network paths and ensure fast failure
detection, enhancing network resilience.
Which route is preferred by the Junos OS software routing tables?
Correct Answer:
C
In Junos OS,direct routesare the most preferred routes in the routing table, having the highest priority.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Direct Routes:
Direct routes represent networks that are directly connected to the router's interfaces. Since these routes are directly accessible, they are assigned the highest priority and always take precedence over other types of routes.
Preference Values:
Direct routes have apreference of 0, which is the most preferred in Junos. Static routes, OSPF routes, and BGP routes have higher preference values and will only be used if there are no direct routes to the destination.
Juniper Reference:
Direct Route Preference: In Junos,direct routesare always preferred over other routes, ensuring that the router forwards traffic through locally connected networks.

