You are setting up a customer's 15 headless loT devices that do not support 802.1X. What should you use?
Correct Answer:
A
MPSK Local is a feature that can be used to set up 15 headless IoT devices that do not support 802.1X authentication. MPSK Local allows the switch to automatically generate and assign unique pre-shared keys for devices based on their MAC addresses, without requiring any configuration on the devices or an external authentication server. The other options are incorrect because they either require 802.1X authentication, which is not supported by the IoT devices, or WPA3 encryption, which is not supported by Aruba CX switches. References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS- CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/bk01-ch05.html https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/bk01- ch06.html
What is the best practice for handling voice traffic with dynamic segmentation on AOS-CX switches?
Correct Answer:
A
This is the best practice for handling voice traffic with dynamic segmentation on AOS-CX switches. Dynamic segmentation is a feature that allows AOS-CX switches to tunnel user traffic to a controller or another switch based on user roles and policies. For voice traffic, it is recommended to use switch authentication and local forwarding, which means the voice devices are authenticated by the switch and their traffic is forwarded locally without tunneling. This reduces latency and jitter for voice traffic and improves voice quality. The other options are incorrect because they either use central authentication or tunneling, which are not optimal for voice traffic. References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/bk01- ch05.html https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_AOS-CX.pdf
Which statements regarding Aruba NAE agents are true? (Select two )
Correct Answer:
AC
The statements that are true regarding Aruba NAE agents are A and C.
* A. A single NAE script can be used by multiple NAE agents. This means that you can create different instances of the same script with different parameters or settings. For example, you can use the same script to monitor different VLANs or interfaces on the switch1.
* C. NAE agents will never consume more than 10% of switch processor resources. This is a built-in safeguard that prevents the agents from affecting the switch performance or stability. If an agent exceeds the 10% limit, it will be automatically disabled and an alert will be generated2.
The other options are incorrect because:
✑ B. NAE agents are not active at all times. They can be enabled or disabled by the user, either manually or based on a schedule. They can also be disabled automatically if they encounter an error or exceed the resource limit1.
✑ D. NAE scripts do not need to be reviewed and signed by Aruba before being used. You can create your own custom scripts using Python and upload them to the switch or Aruba Central. You can also use the scripts provided by Aruba or other sources, as long as they are compatible with the switch firmware version1.
✑ E. A single NAE agent cannot be used by multiple NAE scripts. An agent is an instance of a script that runs on the switch. Each agent can only run one script at a time1.
Refer to Exhibit: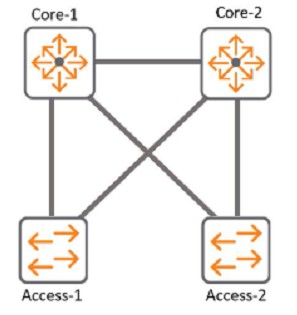
With Access-1, What needs to be identically configured With MSTP to load-balance VLANS?
Correct Answer:
B
The correct answer is B. Spanning-tree instance VLAN mapping.
To load-balance VLANs with MSTP, you need to configure the same VLAN-to-instance mapping on all switches in the same MST region. This means that you need to assign different VLANs to different MST instances, and then adjust the spanning tree parameters (such as priority, cost, or port role) for each instance to achieve the desired load balancing. For example, you can make one switch the root for instance 1 and another switch the root for instance 2, and then map half of the VLANs to instance 1 and the other half to instance 2.
According to the Cisco document Understand the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s), one of the steps to configure MST is:
✑ Split your set of VLANs into more instances and configure different MST settings for each of these instances. In order to easily achieve this, elect Bridge D1 to be the root for VLANs 501 through 1000, and Bridge D2 to be the root for VLANs 1 through 500. These statements are true for this configuration:
Switch D1(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration Switch D1(config-mst)#instance 1 vlan 501-1000 Switch D1(config-mst)#exit
Switch D1(config)#spanning-tree mst 1 priority 0
Switch D2(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration Switch D2(config-mst)#instance 2 vlan 1-500 Switch D2(config-mst)#exit
Switch D2(config)#spanning-tree mst 2 priority 0
The above commands create two MST instances, 1 and 2, and map VLANs 501-1000 to instance 1 and VLANs 1-500 to instance 2. Then, they make switch D1 the root for instance 1 and switch D2 the root for instance 2.
The other options are incorrect because:
✑ A. Spanning-tree bpdu-guard setting is a security feature that disables a port if it receives a BPDU from an unauthorized device. It does not affect load balancing with MSTP.
✑ C. Spanning-tree CIST mapping is not a valid command. CIST stands for Common and Internal Spanning Tree, which is the spanning tree instance that runs within an MST region and interacts with other regions or non-MST switches.
✑ D. Spanning-tree root-guard setting is another security feature that prevents a port from becoming a root port if it receives superior BPDUs from another switch. It does not affect load balancing with MSTP.
A customer is concerned about me unprotected traffic between an AOS-CX switch and a gateway, running on AOStO. What is a feasible option to protect this traffic?
Correct Answer:
A
According to the Aruba Documentation Portal1, PAPI (Port Aggregation Protocol) is a protocol that allows multiple physical ports to be aggregated into a single logical port for increased bandwidth and performance. PAPI can be used between AOS-CX switches and gateways, or between AOS-CX switches and other devices.
Option A: Implement an IPSec tunnel to protect PAPI between the AOS-CX switches and the gateway
This is because option A shows how to implement an IPSec tunnel between two devices using the interface command and the ipsec command. An IPSec tunnel can provide encryption and authentication for PAPI traffic between two devices, such as an AOS-CX switch and a gateway2.
Therefore, option A is a feasible option to protect this traffic.
I hope this helps you. If you need more information, please let me know. 1: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.06/HTML/5200-
7727/Content/Chp_prev_traf_loss/Act_gtw_act_fwd/act-gat-ove-vsx-10.htm 2: https://community.arubanetworks.com/blogviewer?blogkey=989fc43a-e0df-42db-9c0b- f96d6565a1fa

