What will be the result of reverting to a previous revision version in the revision history?
Correct Answer:
C
✑ Option C: It will modify the device-level database.This is correct. Reverting to a previous revision version in the revision history affects the device-level database by restoring it to the state saved in the selected revision. This ensures that any changes made after the selected revision are discarded, and the device configuration is returned to the earlier state.
Explanation of Incorrect Options:
✑ Option A: It will install configuration changes to managed devices automaticallyis incorrect because reverting a revision does not automatically push changes to the devices; it merely reverts the configuration on the FortiManager.
✑ Option B: It will tag the device settings status as Auto-Updateis incorrect because "Auto-Update" is not a status related to the revision history mechanism.
✑ Option D: It will generate a new version ID and remove all other revision history versionsis incorrect as reverting to a previous revision does not delete all other versions; it creates a new revision point for tracking.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to the "Revision Management" section in the FortiManager Administration Guide, which provides an overview of how revisions are managed and utilized for restoring configurations.
Refer to the exhibit.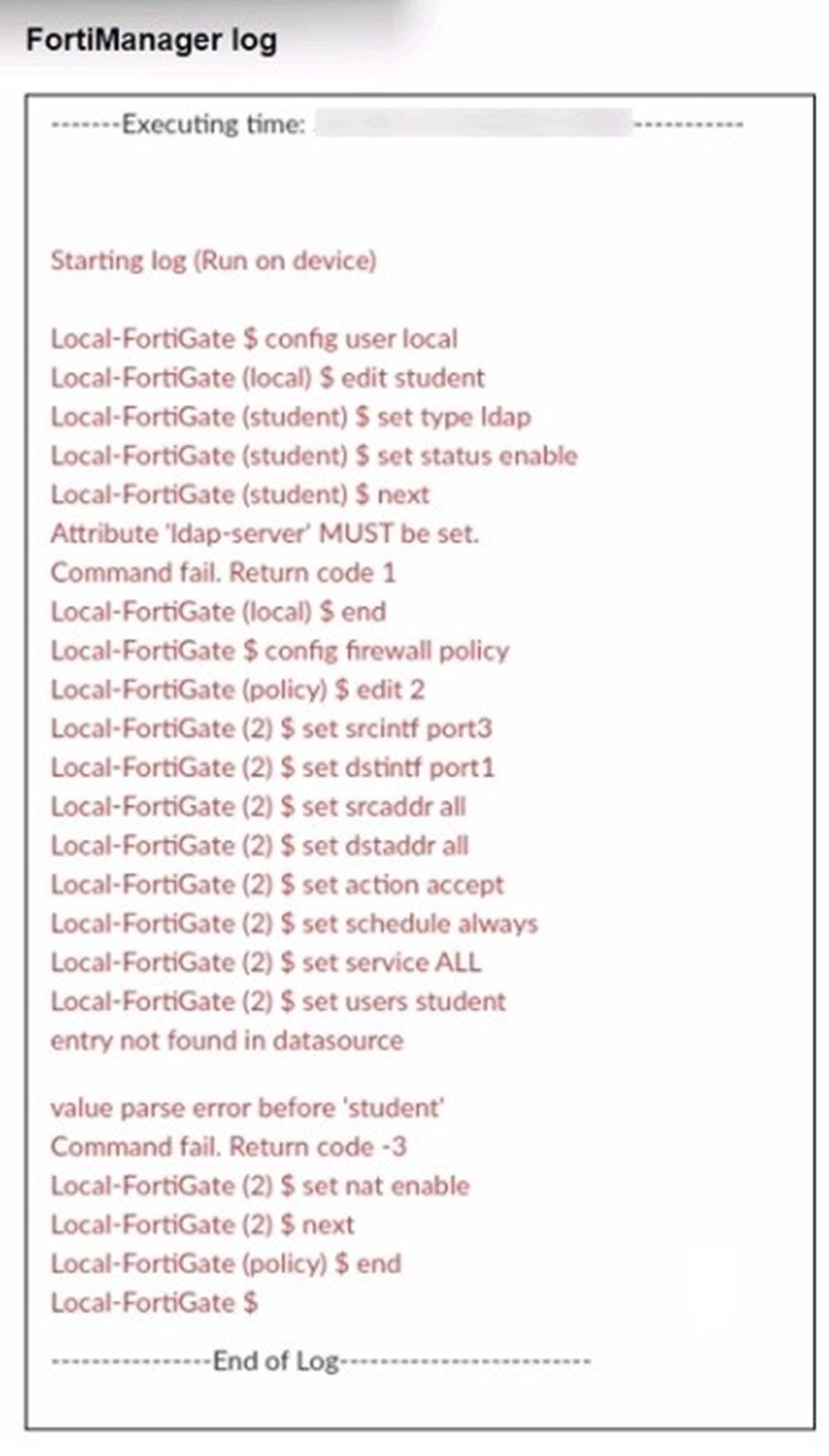
Correct Answer:
B
From the log provided in the exhibit, several conclusions can be drawn regarding the installation of Policy ID 2:
✑ The installation process fails when attempting to set theLDAP user "student". The log shows:
Because of these errors, while other configuration elements (such as source and destination interfaces, actions, and services) are properly set, the user configuration for "student"isnot applied.
Evaluation of the answer options:
✑ A. Policy ID 2 is installed in the disabled state.
✑ B. Policy ID 2 is installed without the remote user student.
✑ C. Policy ID 2 will not be installed.
✑ D. Policy ID 2 is installed without a source address.
From the log exhibit, we see errors related to the "ldap-server" attribute not being set and an error with the entry "student" not being found in the datasource. This indicates that Policy ID 2 will not be installed due to missing or incorrect data required for successful installation. The "Command fail. Return code -3" confirms the installation failure, so the correct answer is C.
Options A, B, and D are incorrect because:
✑ A suggests the policy is installed in a disabled state, which isn't supported by the log.
✑ B and D suggest partial installation, but the error messages indicate a complete failure to install Policy ID 2.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to FortiManager 7.4 Troubleshooting Guide: Common Errors and Log Interpretation.
An administrator is in the process of copying a system template profile between ADOMs by running the following command: execute fmprofile import-profile ADOM2 3547 /tmp/myfile Where does this command import the system template profile from?
Correct Answer:
A
The commandexecute fmprofile import-profile ADOM2 3547 /tmp/myfileis used to import a system template profile from the FortiManager file system. The path/tmp/myfileindicates a location in the FortiManager's local file system, from which the profile will be imported into the specified ADOM.
Options B, C, and D are incorrect because:
✑ B, C, and Dsuggest importing from different databases, which is not accurate since the command explicitly refers to the file system location.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to FortiManager 7.4 CLI Reference Guide: Commands for Profile Management.
Which configuration setting for FortiGate is part o an ADOM-level database on FortiManager?
Correct Answer:
B
✑ Option B: Routingis the correct answer. The ADOM-level database in FortiManager stores configuration settings such as routing, firewall policies, and objects that are shared across multiple devices in the ADOM.
Explanation of Incorrect Options:
✑ Option A: NSX-T Service Templateis incorrect as it is not a FortiGate-specific setting managed at the ADOM level.
✑ Option C: SNMPis incorrect because SNMP settings are typically managed on a per-device basis.
✑ Option D: Security profilesis incorrect because security profiles are generally device-level configurations, not ADOM-level.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to "FortiManager Administration Guide" for further details on ADOM-level and device-level configurations.
Which statement about the policy lock feature on FortiManager is true?
Correct Answer:
A
The statement that is true about the policy lock feature on FortiManager is:
✑ A. Policy locking is available in workspace normal mode.
In FortiManager, when working in "workspace-mode normal," policies can be locked by administrators to prevent other administrators from editing them simultaneously. This ensures that only one administrator makes changes at any given time, reducing conflicts or mistakes due to concurrent modifications.
Statements B, C, and D are incorrect because:
✑ B is incorrect since locking a policy does not override a locked ADOM. The ADOM lock takes precedence.
✑ C is incorrect because when a policy is locked, it does not necessarily mean the ADOM is locked.
✑ D is incorrect because administrators in the approval group cannot work concurrently on a locked policy; the policy lock prevents concurrent modifications.
FortiManager References:
✑ Refer to FortiManager 7.4 Administrator Guide: Policy and Objects > Policy Locking to understand how the policy lock feature functions in different workspace modes.

