Refer to the exhibits.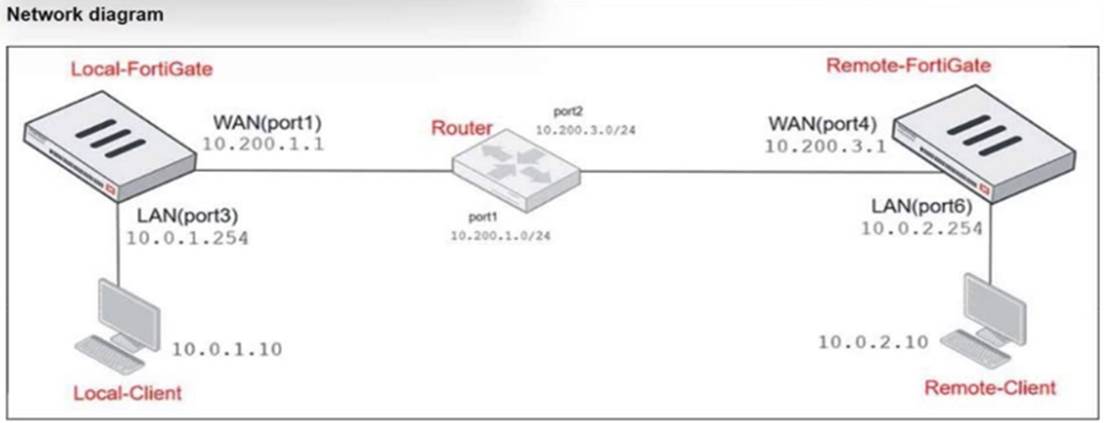
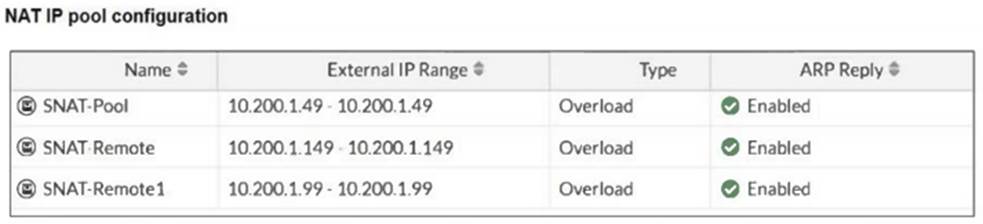
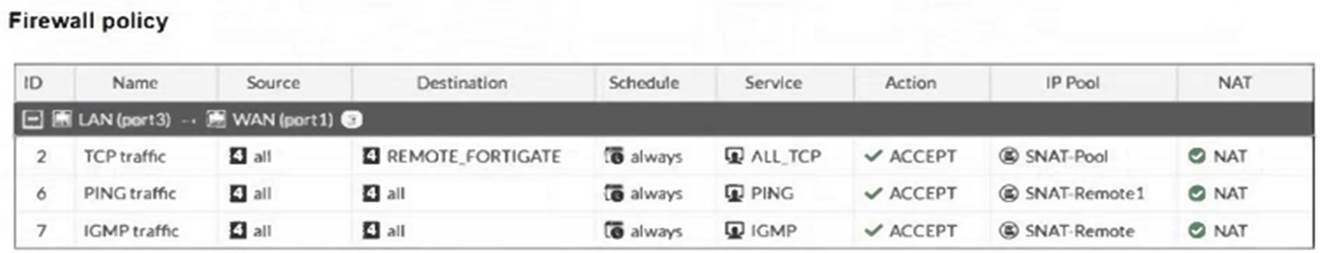
The exhibits show a diagram of a FortiGate device connected to the network, as well as the IP pool configuration and firewall policy objects.
The WAN (port1) interface has the IP address 10.200.1.1/24. The LAN (port3) interface has the IPaddress 10.0.1.254/24.
Which IP address will be used to source NAT (SNAT) the traffic, if the user on Local-Client (10.0.1.10) pings the IP address of Remote-FortiGate (10.200.3.1)?
Correct Answer:
C
The traffic from the user on Local-Client (10.0.1.10) pinging the IP address of Remote-FortiGate (10.200.3.1) will match the firewall policy with the service "PING traffic". According to the firewall policy: Policy ID 6 is set for PING traffic and uses the NAT IP pool "SNAT-Remote1", which is defined as 10.200.1.99.
Policy ID 6 is set for PING traffic and uses the NAT IP pool "SNAT-Remote1", which is defined as 10.200.1.99.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial configuration from the remote authentication server.
Why does the FortiGate administrator need this configuration?
Correct Answer:
A
Refer to the exhibit showing a FortiGuard connection debug output.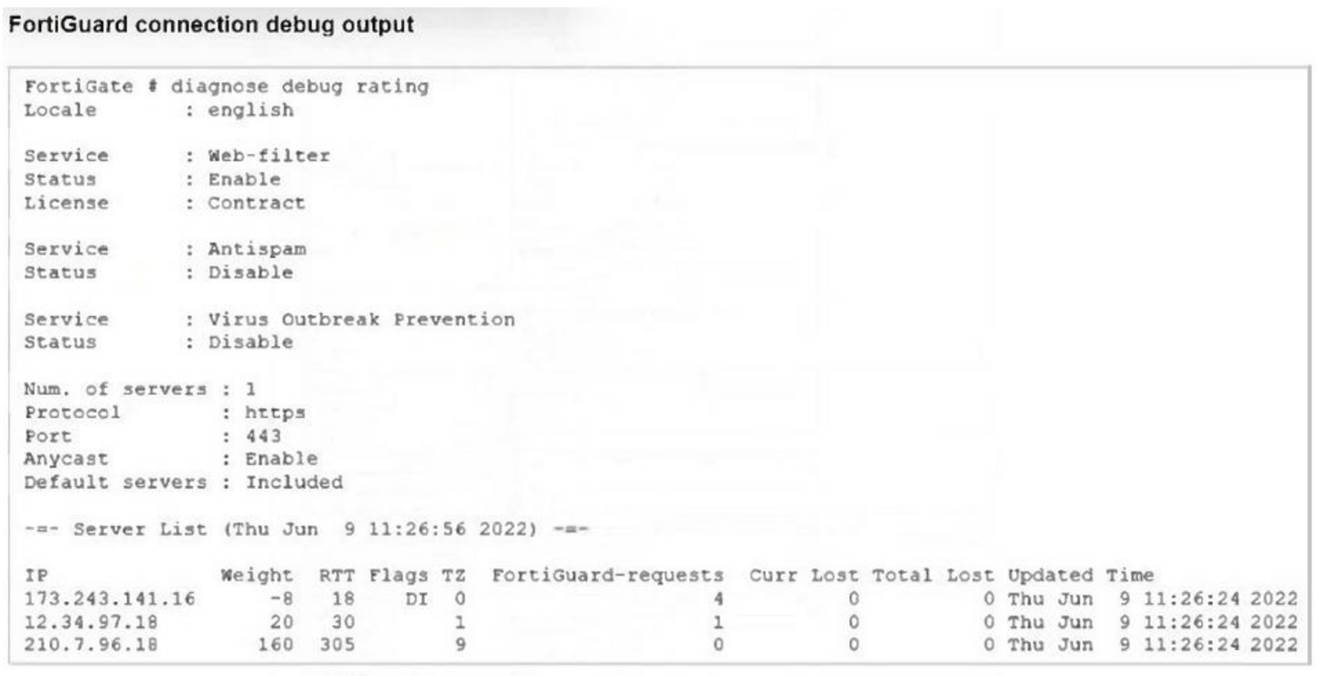
Based on the output, which two facts does the administrator know about the FortiGuard connection? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AD
The debug output indicates that FortiGate connected to one server (173.243.141.16) to retrieve contract information as it shows four FortiGuard requests without any packet loss, which confirms the connection to the server. Additionally, the default FortiGuard communication settings are being used, as indicated by the use of the HTTPS protocol on port 443, which is the default setting for FortiGuard connections.
References: FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: FortiGuard Connection Settings
FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: FortiGuard Connection Settings
An administrator configures FortiGuard servers as DNS servers on FortiGate using default settings. What is true about the DNS connection to a FortiGuard server?
Correct Answer:
D
By default, DNS queries to FortiGuard servers use UDP port 53.
Refer to the exhibit.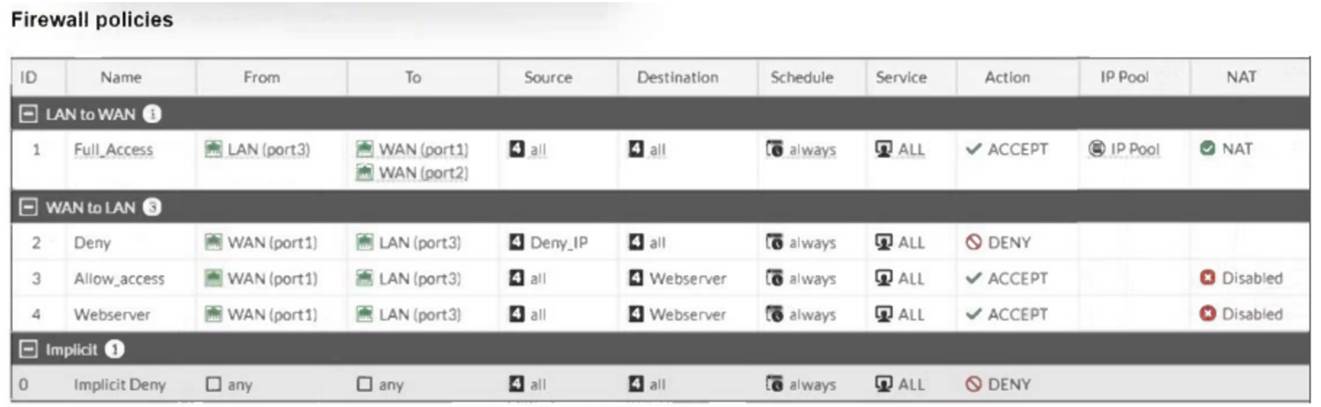
Which statement about this firewall policy list is true?
Correct Answer:
C
The firewall policy list in the exhibit is arranged in the "Interface Pair View," where policies are grouped by
their incoming (ingress) and outgoing (egress) interface pairs. Each section (LAN to WAN, WAN to LAN,
etc.) groups policies based on these interface pairings. This view helps administrators quickly identify which
policies apply to specific traffic flows between network interfaces. Options A and D are incorrect because the Implicit group typically does not include more than one deny policy, and there is no "sequence grouping
view" in FortiGate. Option B is incorrect as the list is not displayed strictly by ID sequence.
References:
FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: Firewall Policy Views

