Atypical generic skill required for the role of tester is the ability to
Correct Answer:
C
A key skill for testers is the ability to use various tools to automate repetitive tasks, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of testing processes. This includes tools for test execution, test management, and defect tracking. The ISTQB CTFL Syllabus v4.0 emphasizes the importance of using tools to improve productivity and reduce manual effort in repetitive testing tasks, making this a critical skill for testers.
Which of the following statements is true?
Correct Answer:
C
Experience-based test techniques are test design techniques that rely on the experience, knowledge, intuition, and creativity of the testers to identify and execute test cases that are likely to find defects in the software system. Experience-based test techniques are often useful to detect hidden defects that have not been targeted by black- box test techniques, which are test design techniques that use the external behavior and specifications of the software system as the test basis, without considering its internal structure or implementation. Experience-based test techniques can complement black-box test techniques by covering aspects that are not explicitly specified, such as usability, security, reliability, performance, etc. The other statements are false, because:
✑ Experience-based test techniques do not rely on the experience of testers to identify the root causes of defects found by black-box test techniques, but rather to identify the potential sources of defects based on their own insights, heuristics, or exploratory testing. The root causes of defects are usually identified by debugging or root cause analysis, which are activities that involve examining the code or the development process to find and fix the errors that led to the defects.
✑ Some of the most common test basis used by white-box test techniques include
the source code, the design documents, the architecture diagrams, and the control flow graphs of the software system. White-box test techniques are test design techniques that use the internal structure and implementation of the software system as the test basis, and aim to achieve a certain level of test coverage based on the code elements, such as statements, branches, paths, etc. User stories, use cases, and business processes are examples of test basis used by black-box test techniques, as they describe the functional and non-functional requirements of the software system from the perspective of the users or the stakeholders.
✑ The primary goal of experience-based test techniques is not to design test cases
that can be easily automated using a GUI-based test automation tool, but rather to design test cases that can reveal defects that are not easily detected by other test techniques, such as boundary value analysis, equivalence partitioning, state transition testing, etc. Test automation is the use of software tools to execute test cases and compare actual results with expected results, without human intervention. Test automation can be applied to different types of testtechniques, depending on the test objectives, the test levels, the test tools, and the test resources. However, test automation is not always feasible or beneficial, especially for test cases that require human judgment, creativity, or exploration, such as
those designed by experience-based test techniques. References: ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level (CTFL) v4.0 sources and documents:
✑ ISTQB® Certified Tester Foundation Level Syllabus v4.0, Chapter 2.2.1, Black-box
Test Design Techniques
✑ ISTQB® Certified Tester Foundation Level Syllabus v4.0, Chapter 2.2.2, White- box Test Design Techniques
✑ ISTQB® Certified Tester Foundation Level Syllabus v4.0, Chapter 2.2.3, Experience-based Test Design Techniques
✑ ISTQB® Glossary of Testing Terms v4.0, Experience-based Test Technique, Black-box Test Technique, White-box Test Technique, Test Basis, Test Coverage, Test Automation
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Correct Answer:
B
Acceptance criteria for user stories often include detailed specifications about data definitions, such as the format, allowed values, and default values for a data item. This helps ensure that the developed feature meets the expected requirements and provides a clear understanding for both developers and testers on what needs to be validated. Therefore, statement B is true as per the ISTQB CTFL syllabus.
You are testing a system that is used in motor vehicles to warn the driver of an obstacle when re-versing. Output is provided by a series of LED lights (green, yellow, and red), each illuminated based on clearly defined conditions.
The following summary describes the functionality:
•Object within 10 metres, green LED lit.
•Object within 5 metres, yellow LED lit.
•Object within 1 metre, red LED lit.
•Setting sensitivity mode to "ON" will result in only the red LED being lit when the object is within 1 metre.
The following decision table describes the rules associated with the functioning of this proximity warning system: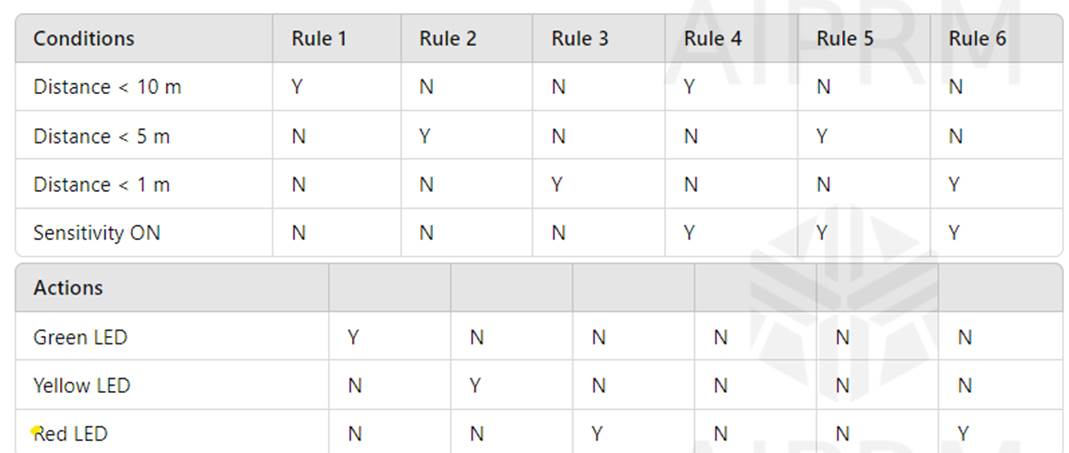
Which intended functionality is tested by Rule 5 in the decision table?
Correct Answer:
D
Rule 5 in the decision table indicates that when the object is within 5 metres of the vehicle and the sensitivity mode is switched "on", no LED is lit. This matches the conditions and actions described in the decision table provided, ensuring that only the red LED is lit when the sensitivity mode is on and the object is within 1 metre, otherwise no LED is lit .
You are performing the role of tester on an Agile project. Which of the following tasks would be your responsibility?
Correct Answer:
A
In an Agile project, a tester's responsibilities include understanding, implementing, and updating the test strategy (i), actively collaborating with developers and business stakeholders to clarify requirements, especially in terms of testability, consistency, and completeness (iv), and participating proactively in team retrospective meetings, suggesting and implementing improvements (v). These activities ensure that testing is integrated into the development process, promoting continuous feedback and improvement. The ISTQB CTFL syllabus underlines the collaborative nature of Agile testing and the tester's role in contributing to the team's overall quality goals.
References:ISTQB CTFL Syllabus, Section on Agile Testing Practices.

