While reviewing web server logs, an analyst notices several entries with the same time stamps, but all contain odd characters in the request line. Which of the following steps should be taken next?
Correct Answer:
B
Determining what attack the odd characters are indicative of is the next step that should be taken after reviewing web server logs and noticing several entries with the same time stamps, but all contain odd characters in the request line. This step can help the analyst identify the type and severity of the attack, as well as the possible source and motive of the attacker. The odd characters in the request line may indicate that the attacker is trying to exploit a vulnerability or inject malicious code into the web server or application, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, buffer overflow, or command injection. The analyst can use tools and techniques such as log analysis, pattern matching, signature detection, or threat intelligence to determine what attack the odd characters are indicative of, and then proceed to the next steps of incident response, such as containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned. Official References:
✑ https://partners.comptia.org/docs/default-source/resources/comptia-cysa-cs0-002-exam-objectives
✑ https://www.comptia.org/certifications/cybersecurity-analyst
✑ https://www.comptia.org/blog/the-new-comptia-cybersecurity-analyst-your- questions-answered
Which of the following security operations tasks are ideal for automation?
Correct Answer:
D
Email header analysis is one of the security operations tasks that are ideal for automation. Email header analysis involves checking the email header for various indicators of phishing or spamming attempts, such as sender address spoofing, mismatched domains, suspicious subject lines, or phishing confidence metrics. Email header analysis can be automated using tools or scripts that can parse and analyze email headers and take appropriate actions based on predefined rules or thresholds
An analyst is conducting routine vulnerability assessments on the company infrastructure. When performing these scans, a business-critical server crashes, and the cause is traced back to the vulnerability scanner. Which of the following is the cause of this issue?
Correct Answer:
B
The scanner is running in active mode, which is the cause of this issue. Active mode is a type of vulnerability scanning that sends probes or requests to the target systems to test their responses and identify potential vulnerabilities. Active mode can provide more accurate and comprehensive results, but it can also cause more network traffic, performance degradation, or system instability. In some cases, active mode can trigger denial-of-service (DoS) conditions or crash the target systems, especially if they are not configured to handle the scanning requests or if they have underlying vulnerabilities that can be exploited by the scanner12. Therefore, the analyst should use caution when performing active mode scanning, and avoid scanning business-critical or sensitive systems without proper authorization and preparation3. References: Vulnerability Scanning for my Server - Spiceworks Community, Negative Impacts of Automated Vulnerability Scanners and How … - Acunetix, Vulnerability Scanning Best Practices
During an internal code review, software called "ACE" was discovered to have a vulnerability that allows the execution of arbitrary code. The vulnerability is in a legacy, third-party vendor resource that is used by the ACE software. ACE is used worldwide and is essential for many businesses in this industry. Developers informed the Chief Information Security Officer that removal of the vulnerability will take time. Which of the following is the first action to take?
Correct Answer:
D
A compensating control is an alternative measure that provides a similar level of protection as the original control, but is used when the original control is not feasible or cost-effective. In this case, the CISO should develop a compensating control to mitigate the risk of the vulnerability in the ACE software, such as implementing additional monitoring, firewall rules, or encryption, until the issue can be fixed permanently by the developers. References: CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide: Exam CS0-003, 3rd Edition,
Chapter 5, page 197; CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003 Certification Study Guide, Chapter 5, page 205.
An analyst is evaluating the following vulnerability report: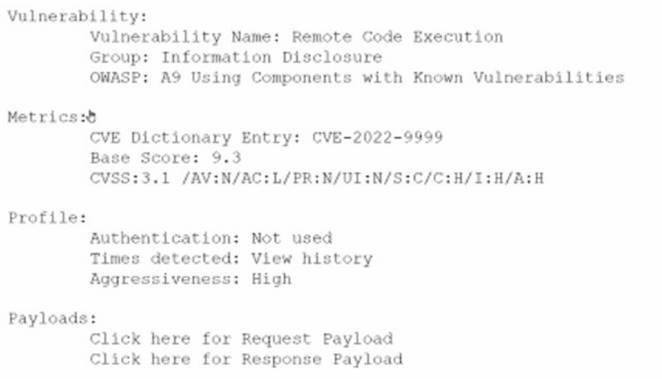
Which of the following vulnerability report sections provides information about the level of impact on data confidentiality if a successful exploitation occurs?
Correct Answer:
B
The correct answer is B. Metrics.
The Metrics section of the vulnerability report provides information about the level of impact on data confidentiality if a successful exploitation occurs. The Metrics section contains the CVE dictionary entry and the CVSS base score of the vulnerability. CVE stands for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures and it is a standardized system for identifying and naming vulnerabilities. CVSS stands for Common Vulnerability Scoring System and it is a standardized system for measuring and rating the severity of vulnerabilities.
The CVSS base score is a numerical value between 0 and 10 that reflects the intrinsic characteristics of a vulnerability, such as its exploitability, impact, and scope. The CVSS base score is composed of three metric groups: Base, Temporal, and Environmental. The Base metric group captures the characteristics of a vulnerability that are constant over time and across user environments. The Base metric group consists of six metrics: Attack Vector, Attack Complexity, Privileges Required, User Interaction, Scope, and Impact. The Impact metric measures the effect of a vulnerability on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the affected resources.
In this case, the CVSS base score of the vulnerability is 9.8, which indicates a critical severity level. The Impact metric of the CVSS base score is 6.0, which indicates a high impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Therefore, the Metrics section provides information about the level of impact on data confidentiality if a successful exploitation occurs.
The other sections of the vulnerability report do not provide information about the level of impact on data confidentiality if a successful exploitation occurs. The Payloads section contains links to request and response payloads that demonstrate how the vulnerability can be exploited. The Payloads section can help an analyst to understand how the attack works, but it does not provide a quantitative measure of the impact. The Vulnerability section contains information about the type, group, and description of the vulnerability. The Vulnerability section can help an analyst to identify and classify the vulnerability, but it does not provide a numerical value of the impact. The Profile section contains information about the authentication, times viewed, and aggressiveness of the vulnerability. The Profile section can help an analyst to assess the risk and priority of the vulnerability, but it does not provide a specific measure of the impact on data confidentiality.
References:
✑ [1] CVE - Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
✑ [2] Common Vulnerability Scoring System SIG
✑ [3] CVSS v3.1 Specification Document
✑ [4] CVSS v3.1 User Guide
✑ [5] How to Read a Vulnerability Report - Security Boulevard

