Which of the following should be updated after a lessons-learned review?
Correct Answer:
D
A lessons-learned review is a process of evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of the incident response plan after an incident or an exercise. The purpose of the review is to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the incident response plan, and to update it accordingly to improve the future performance and resilience of the organization. Therefore, the incident response plan should be updated after a lessons-learned review. References: The answer was based on the NCSC CAF guidance from the National Cyber Security Centre, which states: “You should use post-incident and post-exercise reviews to actively reduce the risks associated with the same, or similar, incidents happening in future.
Lessons learned can inform any aspect of your cyber security, including: System configuration Security monitoring and reporting Investigation procedures Containment/recovery strategies”
A software developer has been deploying web applications with common security risks to include insufficient logging capabilities. Which of the following actions would be most effective to
reduce risks associated with the application development?
Correct Answer:
D
Conducting regular code reviews using OWASP best practices is the most effective action to reduce risks associated with the application development. Code reviews are a systematic examination of the source code of an application to detect and fix errors, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses that may compromise the security, functionality, or performance of the application. Code reviews can help to improve the quality and security of the code, as well as to identify and remediate common security risks, such as insufficient logging capabilities. OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) is a global nonprofit organization that provides free and open resources, tools, standards, and best practices for web application security. OWASP best practices for logging include following a common logging format and approach, logging relevant security events and data, protecting log data from unauthorized access or modification, and using log analysis and monitoring tools to detect and respond to security incidents. By following OWASP best practices for logging, developers can ensure that their web applications have sufficient and effective logging capabilities that can help to prevent, detect, and mitigate security threats.
References: OWASP Logging Cheat Sheet, OWASP Logging Guide, C9: Implement Security Logging and Monitoring - OWASP Foundation
A vulnerability management team is unable to patch all vulnerabilities found during their weekly scans. Using the third-party scoring system described below, the team patches the most urgent vulnerabilities: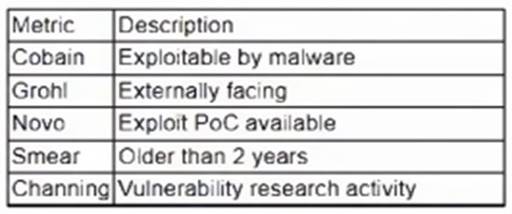
Additionally, the vulnerability management team feels that the metrics Smear and Channing are less important than the others, so these will be lower in priority. Which of the following vulnerabilities should be patched first, given the above third-party scoring system?
Correct Answer:
B
The vulnerability that should be patched first, given the above third-party scoring system, is:
TSpirit: Cobain: Yes Grohl: Yes Novo: Yes Smear: No Channing: No
This vulnerability has three out of five metrics marked as Yes, which indicates a high severity level. The metrics Cobain, Grohl, and Novo are more important than Smear and Channing, according to the vulnerability management team. Therefore, this vulnerability poses a greater risk than the other vulnerabilities and should be patched first.
New employees in an organization have been consistently plugging in personal webcams despite the company policy prohibiting use of personal devices. The SOC manager discovers that new employees are not aware of the company policy. Which of the following will the SOC manager most likely recommend to help ensure new employees are accountable for following the company policy?
Correct Answer:
D
The best action that the SOC manager can recommend to help ensure new employees are accountable for following the company policy is to require all new employees to sign a user agreement to acknowledge the company security policy. A user agreement is a document that defines the rights and responsibilities of the users regarding the use of the company’s systems, networks, or resources, as well as the consequences of violating the company’s security policy. Signing a user agreement can help ensure new employees are aware of and agree to comply with the company security policy, as well as hold them accountable for any breaches or incidents caused by their actions or inactions.
During an incident, analysts need to rapidly investigate by the investigation and leadership teams. Which of the following best describes how PII should be safeguarded during an
incident?
Correct Answer:
B
The best option to safeguard PII during an incident is to ensure permissions are limited in the investigation team and encrypt the data. This is because limiting permissions reduces the risk of unauthorized access or leakage of sensitive data, and encryption protects the data from being read or modified by anyone who does not have the decryption key. Option A is not correct because closing the data may hinder the investigation process and prevent collaboration with other parties who may need access to the data. Option C is not correct because deleting data that is no longer needed may violate legal or regulatory requirements for data retention, and may also destroy potential evidence for the incident. Option D is not correct because opening permissions to the company may expose the data to more people than necessary, increasing the risk of compromise or misuse.
References: CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide: Exam CS0-002, 2nd Edition, Chapter 4, “Data Protection and Privacy Practices”, page 195; CompTIA CySA+ Certification Exam Objectives Version 4.0, Domain 4.0 “Compliance and Assessment”, Objective 4.1 “Given a scenario, analyze data as part of a security incident”, Sub-objective “Data encryption”, page 23
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide: Exam CS0-002, 2nd Edition : CompTIA CySA+ Certification Exam Objectives Version 4.0.pdf)

