Which two pieces of information should you include when you initially create a support ticket? (Choose 2.)
Correct Answer:
AC
✑ Statement A: "A detailed description of the fault." This is essential for support staff to understand the nature of the problem and begin troubleshooting effectively.
✑ Statement C: "A description of the conditions when the fault occurs." This helps in reproducing the issue and identifying patterns that might indicate the cause of the fault.
✑ Statement B: "Details about the computers connected to the network." While useful, this is not as immediately critical as understanding the fault itself and the conditions under which it occurs.
✑ Statement D: "The actions taken to resolve the fault." This is important but typically follows the initial report.
✑ Statement E: "The description of the top-down fault-finding procedure." This is more of a troubleshooting methodology than information typically included in an initial support ticket.
References:
✑ Best Practices for Submitting Support Tickets: Support Ticket Guidelines
HOTSPOT
You purchase a new Cisco switch, turn it on, and connect to its console port. You then run the following command: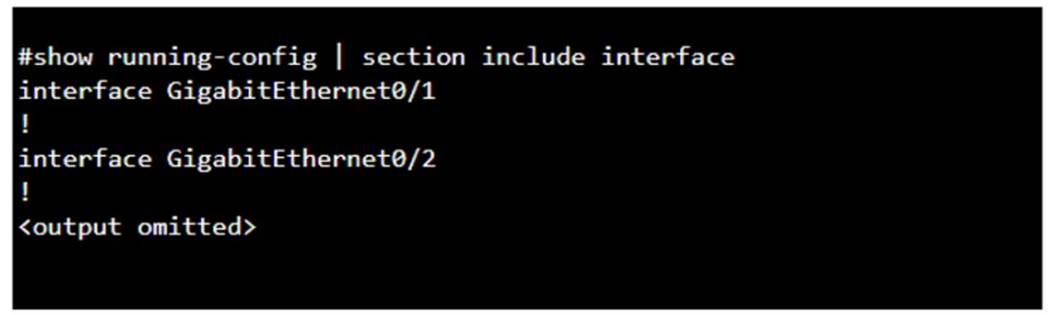
For each statement about the output, select True or False. Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.
Solution:
✑ The two interfaces are administratively shut down:
✑ The two interfaces have default IP addresses assigned:
✑ The two interfaces can communicate over Layer 2:
✑ Interface Status: The absence of the "shutdown" command means the interfaces are not administratively shut down.
✑ IP Address Assignment: There is no evidence in the output that IP addresses have
been assigned to the interfaces, which would typically be shown as "ip address" entries.
✑ Layer 2 Communication: Switch interfaces in their default state operate at Layer 2,
enabling them to forward Ethernet frames and participate in Layer 2 communication.
References:
✑ Cisco IOS Interface Configuration: Cisco Interface Configuration
✑ Understanding Cisco Switch Interfaces: Cisco Switch Interfaces
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:
A
A user reports that a company website is not available. The help desk technician issues a tracert command to determine if the server hosting the website isreachable over the network. The output of the command is shown as follows: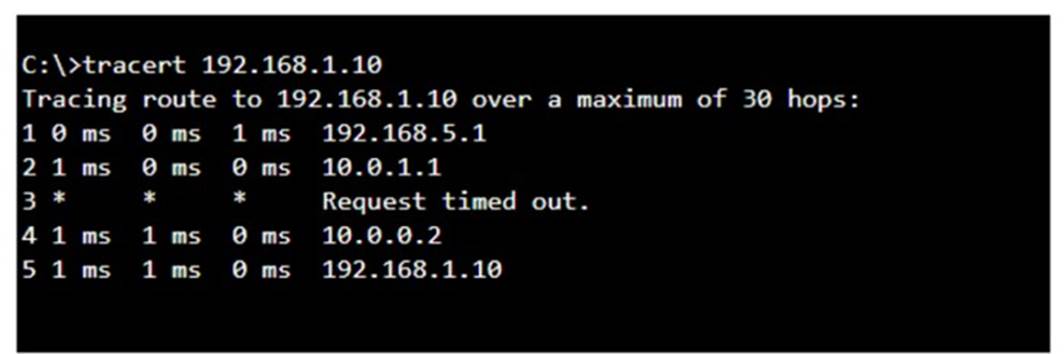
What can you tell from the command output?
Correct Answer:
C
The tracert command output shows the path taken to reach the destination IP address, 192.168.1.10. The command output indicates:
•Hops 1 and 2 are successfully reached.
•Hop 3 times out, meaning the router at hop 3 did not respond to the tracert request. However, this does not necessarily indicate a problem with forwarding packets, as some routers may be configured to block or not respond to ICMP requests.
•Hops 4 and 5 are successfully reached, with hop 5 being the destination IP 192.168.1.10, indicating that the server is reachable.
Thus, the correct answer is C. The server with the address 192.168.1.10 is reachable over the network.
References :=
•Cisco Traceroute Command
•Understanding Traceroute
The tracert command output indicates that the server with the address 192.168.1.10 is reachable over the network. The asterisk (*) at hop 3 suggests that the probe sent to that hop did not return a response, which could be due to a variety of reasons such as a firewall blocking ICMP packets or the router at that hop being configured not to respond to ICMP requests. However, since the subsequent hops (4 and 5) are showing response times, it means that the packets are indeed getting through and the server is reachable12. References :=
•How to Use Traceroute Command to Read Its Results
•How to Use the Tracert Command in Windows
Which two statements are true about the IPv4 address of the default gateway configured on a host? (Choose 2.)
Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.
Correct Answer:
BD
•Statement B: "The same default gateway IPv4 address is configured on each host on the local network." This is true because all hosts on the same local network (subnet) use the same default gateway IP address to send packets destined for other networks.
•Statement D: "The default gateway is the IPv4 address of the router interface connected to the same local network as the host." This is true because the default gateway is the IP address of the router's interface that is directly connected to the local network.
•Statement A: "The IPv4 address of the default gateway must be the first host address in the subnet." This is not necessarily true. The default gateway can be any address within the subnet range.
•Statement C: "The default gateway is the Loopback0 interface IPv4 address of the router connected to the same local network as the host." This is not true; the default gateway is the IP address of the router's physical or logical interface connected to the local network.
•Statement E: "Hosts learn the default gateway IPv4 address through router advertisement messages." This is generally true for IPv6 with Router Advertisement (RA) messages, but not typically how IPv4 hosts learn the default gateway address.
References:
•Cisco Default Gateway Configuration: Cisco Default Gateway
DRAG DROP
Move each protocol from the list on the left to the correct TCP/IP model layer on the right. Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct match.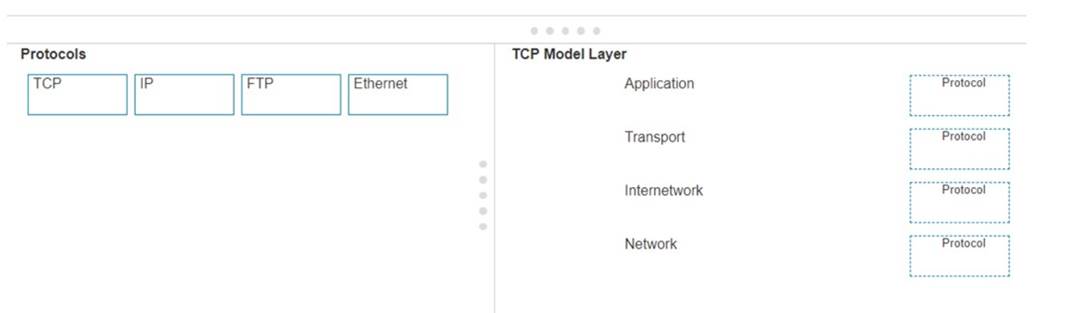
Solution:
Here??s how each protocol aligns with the correct TCP/IP model layer:
✑ TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): This protocol belongs to theTransportlayer, which is responsible for providing communication between applications on different hosts1.
✑ IP (Internet Protocol): IP is part of theInternetworklayer, which is tasked with routing packets across network boundaries to their destination1.
✑ FTP (File Transfer Protocol): FTP operates at theApplicationlayer, which supports application and end-user processes.It is used for transferring files over the network1.
✑ Ethernet: While not a protocol within the TCP/IP stack, Ethernet is associated with theNetwork Interfacelayer, which corresponds to the link layer of the TCP/IP model and is responsible for the physical transmission of data1.
The TCP/IP model layers are designed to work collaboratively to transmit data from one layer to another, with each layer having specific protocols that perform functions necessary for the data transmission process1.
✑ TCP:
✑ IP:
✑ FTP:
✑ Ethernet:
✑ Transport Layer: This layer is responsible for providing communication services directly to the application processes running on different hosts. TCP is a core protocol in this layer.
✑ Internetwork Layer: This layer is responsible for logical addressing, routing, and
packet forwarding. IP is the primary protocol for this layer.
✑ Application Layer: This layer interfaces directly with application processes and provides common network services. FTP is an example of a protocol operating in this layer.
✑ Network Layer: In the TCP/IP model, this layer includes both the data link and physical layers of the OSI model. Ethernet is a protocol used in this layer to define network standards and communication protocols at the data link and physical levels.
References:
✑ TCP/IP Model Overview: Cisco TCP/IP Model
✑ Understanding the TCP/IP Model: TCP/IP Layers
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:
A

