A security analyst is troubleshooting the reason a specific user is having difficulty accessing company resources The analyst reviews the following information: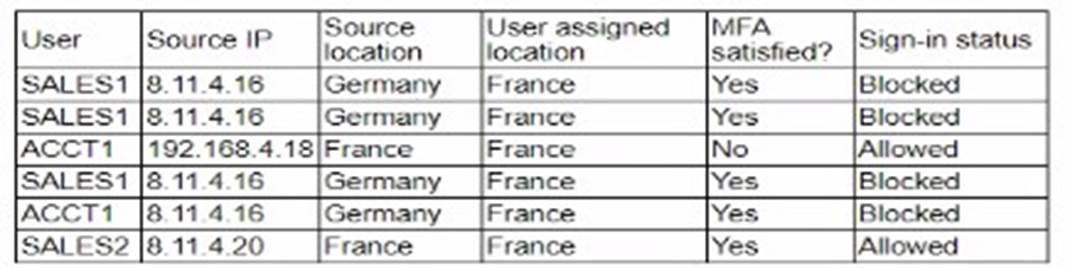
Which of the following is most likely the cause of the issue?
Correct Answer:
B
The table shows that the user "SALES1" is consistently blocked despite having met the MFA requirements. The common factor in these blocked attempts is the source IP address (8.11.4.16) being identified as from Germany while the user is assigned to France. This discrepancy suggests that the network geolocation is being misidentified by the authentication server, causing legitimate access attempts to be blocked.
Why Network Geolocation Misidentification?
✑ Geolocation Accuracy: Authentication systems often use IP geolocation to verify the location of access attempts. Incorrect geolocation data can lead to legitimate requests being denied if they appear to come from unexpected locations.
✑ Security Policies: Company security policies might block access attempts from certain locations to prevent unauthorized access. If the geolocation is wrong, legitimate users can be inadvertently blocked.
✑ Consistent Pattern: The user "SALES1" from the IP address 8.11.4.16 is always blocked, indicating a consistent issue with geolocation.
Other options do not align with the pattern observed:
✑ A. Bypass MFA requirements: MFA is satisfied, so bypassing MFA is not the issue.
✑ C. Administrator access policy: This is about user access, not specific administrator access.
✑ D. OTP codes: The user has satisfied MFA, so OTP code configuration is not the issue.
References:
✑ CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
✑ "Geolocation and Authentication," NIST Special Publication 800-63B
✑ "IP Geolocation Accuracy," Cisco Documentation
Emails that the marketing department is sending to customers are pomp to the customers' spam folders. The security team is investigating the issue and discovers that the certificates used by the email server were reissued, but DNS records had not been updated. Which of the following should the security team update in order to fix this issue? (Select three.)
Correct Answer:
ABC
To prevent emails from being marked as spam, several DNS records related to email authentication need to be properly configured and updated when there are changes to the email server's certificates:
✑ A. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance):
DMARC records help email servers determine how to handle messages that fail SPF or DKIM checks, improving email deliverability and reducing the likelihood of emails being marked as spam.
✑ B. SPF (Sender Policy Framework): SPF records specify which mail servers are authorized to send email on behalf of your domain. Updating the SPF record ensures that the new email server is recognized as an authorized sender.
✑ C. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): DKIM adds a digital signature to email
headers, allowing the receiving server to verify that the email has not been tampered with and is from an authorized sender. Updating DKIM records ensures that emails are properly signed and authenticated.
✑ D. DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions): DNSSEC adds security
to DNS by enabling DNS responses to be verified. While important for DNS security, it does not directly address the issue of emails being marked as spam.
✑ E. SASC: This is not a relevant standard for this scenario.
✑ F. SAN (Subject Alternative Name): SAN is used in SSL/TLS certificates for securing multiple domain names, not for email delivery issues.
✑ G. SOA (Start of Authority): SOA records are used for DNS zone administration and do not directly impact email deliverability.
✑ H. MX (Mail Exchange): MX records specify the mail servers responsible for receiving email on behalf of a domain. While important, the primary issue here is the authentication of outgoing emails, which is handled by SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
References:
✑ CompTIA Security+ Study Guide
✑ RFC 7208 (SPF), RFC 6376 (DKIM), and RFC 7489 (DMARC)
✑ NIST SP 800-45, "Guidelines on Electronic Mail Security"
A company's help desk is experiencing a large number of calls from the finance department slating access issues to www bank com The security operations center reviewed the following security logs: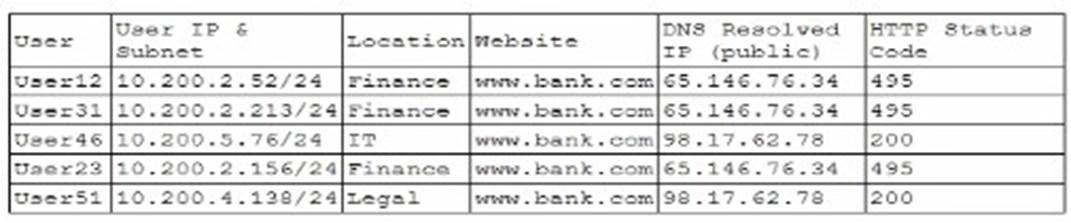
Which of the following is most likely the cause of the issue?
Correct Answer:
C
Sinkholing, or DNS sinkholing, is a method used to redirect malicious traffic to a safe destination. This technique is often employed by security teams to prevent access to malicious domains by substituting a benign destination IP address.
In the given logs, users from the finance department are accessing www.bank.com and receiving HTTP status code 495. This status code is typically indicative of a client certificate error, which can occur if the DNS traffic is being manipulated or redirected incorrectly. The consistency in receiving the same HTTP status code across different users suggests a systematic issue rather than an isolated incident.
✑ Recursive DNS resolution failure (A) would generally lead to inability to resolve
DNS at all, not to a specific HTTP error.
✑ DNS poisoning (B) could result in users being directed to malicious sites, but again, would likely result in a different set of errors or unusual activity.
✑ Incorrect DNS setup (D) would likely cause broader resolution issues rather than targeted errors like the one seen here.
By reviewing the provided data, it is evident that the DNS traffic for www.bank.com is being rerouted improperly, resulting in consistent HTTP 495 errors for the finance department users. Hence, the most likely cause is that the DNS traffic is being sinkholed.
References:
✑ CompTIA SecurityX study materials on DNS security mechanisms.
✑ Standard HTTP status codes and their implications.
An engineering team determines the cost to mitigate certain risks is higher than the asset values The team must ensure the risks are prioritized appropriately. Which of the following is the best way to address the issue?
Correct Answer:
D
When the cost to mitigate certain risks is higher than the asset values, the best approach is to purchase insurance. This method allows the company to transfer the risk to an insurance provider, ensuring that financial losses are covered in the event of an incident. This approach is cost-effective and ensures that risks are prioritized appropriately without overspending on mitigation efforts.
References:
✑ CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide: Discusses risk management strategies, including risk transfer through insurance.
✑ NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF): Highlights the use of insurance as a risk mitigation strategy.
✑ "Information Security Risk Assessment Toolkit" by Mark Talabis and Jason Martin: Covers risk management practices, including the benefits of purchasing insurance.
A cloud engineer needs to identify appropriate solutions to:
• Provide secure access to internal and external cloud resources.
• Eliminate split-tunnel traffic flows.
• Enable identity and access management capabilities.
Which of the following solutions arc the most appropriate? (Select two).
Correct Answer:
CF
To provide secure access to internal and external cloud resources, eliminate split-tunnel traffic flows, and enable identity and access management capabilities, the most appropriate solutions are CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) and SASE (Secure Access Service Edge).
Why CASB and SASE?
✑ CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker):
✑ SASE (Secure Access Service Edge):
Other options, while useful, do not comprehensively address all the requirements:
✑ A. Federation: Useful for identity management but does not eliminate split-tunnel traffic or provide comprehensive security.
✑ B. Microsegmentation: Enhances security within the network but does not directly address secure access to cloud resources or split-tunnel traffic.
✑ D. PAM (Privileged Access Management): Focuses on managing privileged accounts and does not provide comprehensive access control for internal and external resources.
✑ E. SD-WAN: Enhances WAN performance but does not inherently provide the identity and access management capabilities or eliminate split-tunnel traffic.
References:
✑ CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
✑ "CASB: Cloud Access Security Broker," Gartner Research

