For compliance reasons a Security Engineer must produce a weekly report that lists any instance that does not have the latest approved patches applied. The Engineer must also ensure that no system goes more than 30 days without the latest approved updates being applied
What would the MOST efficient way to achieve these goals?
Correct Answer:
B
Amazon EC2 Systems Manager is a service that helps you automatically collect software inventory, apply OS patches, create system images, and configure Windows and Linux operating systems3. You can use Systems Manager to report on instance patch compliance and enforce updates during the defined maintenance windows4. The other options are either inefficient or not feasible for achieving the goals.
A company is building an application on IAM that will store sensitive Information. The company has a support team with access to the IT infrastructure, including databases. The company's security engineer must introduce measures to protect the sensitive data against any data breach while minimizing management overhead. The credentials must be regularly rotated.
What should the security engineer recommend?
Correct Answer:
C
To protect the sensitive data against any data breach and minimize management overhead, the security engineer should recommend the following solution: Enable Amazon RDS encryption to encrypt the database and snapshots. This allows the security engineer to use AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) to encrypt data at rest for the database and any backups or replicas.
Enable Amazon RDS encryption to encrypt the database and snapshots. This allows the security engineer to use AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) to encrypt data at rest for the database and any backups or replicas. Enable Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) encryption on Amazon EC2 instances. This allows the security engineer to use AWS KMS to encrypt data at rest for the EC2 instances and any snapshots or volumes.
Enable Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) encryption on Amazon EC2 instances. This allows the security engineer to use AWS KMS to encrypt data at rest for the EC2 instances and any snapshots or volumes. Store the database credentials in AWS Secrets Manager with automatic rotation. This allows the security engineer to encrypt and manage secrets centrally, and to configure automatic rotation schedules for them.
Store the database credentials in AWS Secrets Manager with automatic rotation. This allows the security engineer to encrypt and manage secrets centrally, and to configure automatic rotation schedules for them. Set up TLS for the connection to the RDS hosted database. This allows the security engineer to encrypt data in transit between the EC2 instances and the database.
Set up TLS for the connection to the RDS hosted database. This allows the security engineer to encrypt data in transit between the EC2 instances and the database.
A company uses identity federation to authenticate users into an identity account (987654321987) where the users assume an IAM role named IdentityRole. The users then assume an IAM role named JobFunctionRole in the target IAM account (123456789123) to perform their job functions.
A user is unable to assume the IAM role in the target account. The policy attached to the role in the identity account is:
What should be done to enable the user to assume the appropriate role in the target account?
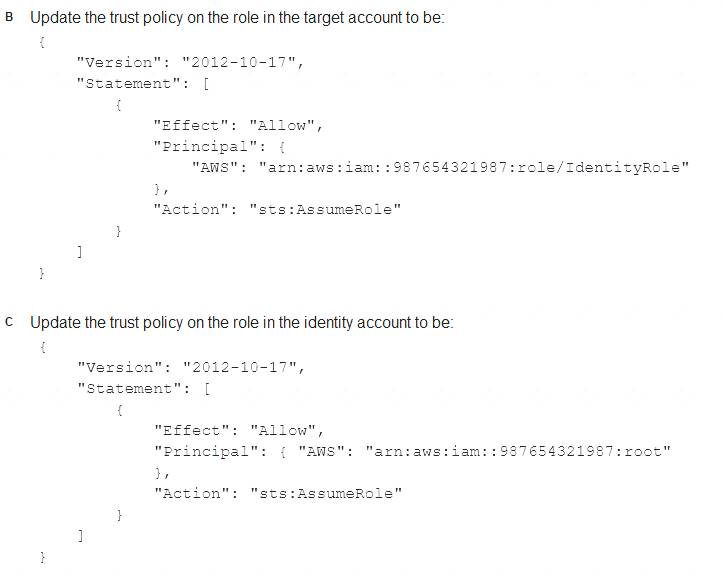

Correct Answer:
B
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/how-to-use-trust-policies-with-iam-roles/
A company is using AWS to run a long-running analysis process on data that is stored in Amazon S3 buckets. The process runs on a fleet of Amazon EC2 instances that are in an Auto Scaling group. The EC2 instances are deployed in a private subnet Of a VPC that does not have internet access. The EC2 instances and the S3 buckets are in the same AWS account
The EC2 instances access the S3 buckets through an S3 gateway endpoint that has the default access policy. Each EC2 instance is associated With an instance profile role that has a policy that explicitly allows the s3:GetObject action and the s3:PutObject action for only the required S3 buckets.
The company learns that one or more of the EC2 instances are compromised and are exfiltrating data to an S3 bucket that is outside the companys organization in AWS Organizations. A security engtneer must implement a solution to stop this exfiltration of data and to keep the EC2 processing job functional.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
Correct Answer:
D
The correct answer is D.
To stop the data exfiltration from the compromised EC2 instances, the security engineer needs to implement a solution that can deny access to any S3 bucket that is outside the company’s organization. The solution should also allow the EC2 instances to access the required S3 buckets within the company’s organization for the analysis process.
Option A is incorrect because updating the policy on the S3 gateway endpoint will not affect the access to S3 buckets that are outside the company’s organization. The S3 gateway endpoint only applies to S3 buckets that are in the same AWS Region as the VPC. The compromised EC2 instances can still access S3 buckets in other Regions or other AWS accounts through the internet gateway or NAT device.
Option B is incorrect because updating the policy on the instance profile role will not prevent the compromised EC2 instances from using other credentials or methods to access S3 buckets outside the company’s organization. The instance profile role only applies to requests that are made using the credentials of that role. The compromised EC2 instances can still use other IAM users, roles, or access keys to access S3 buckets outside the company’s organization.
Option C is incorrect because adding a network ACL rule to block outgoing connections on port 443 will also block legitimate connections to S3 buckets within the company’s organization. The network ACL rule will prevent the EC2 instances from accessing any S3 bucket through HTTPS, regardless of whether it is inside or outside the company’s organization.
Option D is correct because applying an SCP on the AWS account will effectively deny access to any S3 bucket that is outside the company’s organization. The SCP will apply to all IAM users, roles, and resources in the AWS account, regardless of how they access S3. The SCP will use the aws:ResourceOrgID and aws:PrincipalOrgID condition keys to check whether the S3 bucket and the principal belong to the same organization as the AWS account. If they do not match, the SCP will deny the S3 actions.
References: Using service control policies
Using service control policies AWS Organizations service control policy examples
AWS Organizations service control policy examples
A company needs to encrypt all of its data stored in Amazon S3. The company wants to use IAM Key Management Service (IAM KMS) to create and manage its encryption keys. The company's security policies require the ability to Import the company's own key material for the keys, set an expiration date on the keys, and delete keys immediately, if needed.
How should a security engineer set up IAM KMS to meet these requirements?
Correct Answer:
A
To meet the requirements of importing their own key material, setting an expiration date on the keys, and deleting keys immediately, the security engineer should do the following: Configure AWS KMS and use a custom key store. This allows the security engineer to use a key manager outside of AWS KMS that they own and manage, such as an AWS CloudHSM cluster or an external key manager.
Configure AWS KMS and use a custom key store. This allows the security engineer to use a key manager outside of AWS KMS that they own and manage, such as an AWS CloudHSM cluster or an external key manager. Create a customer managed CMK with no key material. Import the company’s keys and key material into the CMK. This allows the security engineer to use their own key material for encryption and decryption operations, and to specify an expiration date for it.
Create a customer managed CMK with no key material. Import the company’s keys and key material into the CMK. This allows the security engineer to use their own key material for encryption and decryption operations, and to specify an expiration date for it.

