- (Topic 2)
Refer to Exhibit:
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic. There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance. As part of examining the router resources, the OSPF DRs need to be known. All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router. Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
DF
There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40)
& Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
- (Topic 6)
Refer to the exhibit.
Which statement describes DLCI 17?
Correct Answer:
C
DLCI stands for Data Link Connection Identifier. DLCI values are used on Frame Relay interfaces to distinguish between different virtual circuits. DLCIs have local significance because, the identifier references the point between the local router and the local Frame Relay switch to which the DLCI is connected.
- (Topic 1)
Which port state is introduced by Rapid-PVST?
Correct Answer:
C
Spanning Tree from PVST+ to Rapid-PVST Migration Configuration Example
Reference 1: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/switches/ps708/products_configuration_example 09186a00807b0670.shtml
Reference 2: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cf a.shtml
PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). But PVST+ has only 3 port states (discarding, learning and forwarding) while STP has 5 port states (blocking, listening, learning, forwarding and disabled). So discarding is a new port state in PVST+.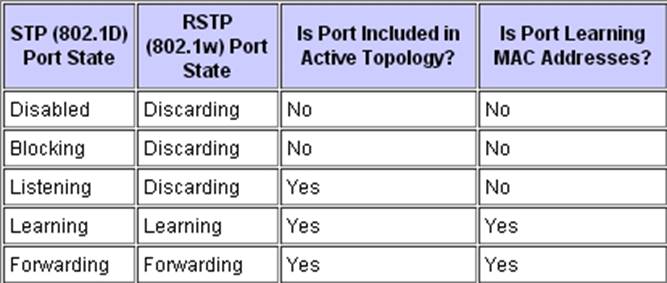
Background Information
802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) has a drawback of slow convergence. Cisco Catalyst switches support three types of STPs, which are PVST+, rapid-PVST+ and MST. PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D standard and includes Cisco proprietary extensions such as BackboneFast, UplinkFast, and PortFast. Rapid-PVST+ is based on IEEE 802.1w standard and has a faster convergence than 802.1D. RSTP (IEEE 802.1w) natively includes most of the Cisco proprietary enhancements to the 802.1D Spanning Tree, such as BackboneFast and UplinkFast. Rapid-PVST+ has these unique features:
Uses Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) version 2 which is backward compatible with the 802.1D STP, which uses BPDU version 0.
All the switches generate BPDUs and send out on all the ports every 2 seconds, whereas in 802.1D STP only the root bridge sends the configuration BPDUs.
Port Roles—Root port, designated port, alternate port and backup port. Port States—Discarding, Learning, and Forwarding.
Port Types—Edge Port (PortFast), Point-to-Point and Shared port.
Rapid-PVST uses RSTP to provide faster convergence. When any RSTP port receives legacy 802.1D BPDU, it falls back to legacy STP and the inherent fast convergence benefits of 802.1w are lost when it interacts with legacy bridges.
- (Topic 5)
What occurs on a Frame Relay network when the CIR is exceeded?
Correct Answer:
D
Committed information rate (CIR): The minimum guaranteed data transfer rate agreed to by the Frame Relay switch. Frames that are sent in excess of the CIR are marked as discard eligible (DE) which means they can be dropped if the congestion occurs within the Frame Relay network.
Note: In the Frame Relay frame format, there is a bit called Discard eligible (DE) bit that is used to identify frames that are first to be dropped when the CIR is exceeded.
CORRECT TEXT - (Topic 6)
A new switch is being added to the River Campus LAN. You will work to complete this process by first configuring the building_2 switch with an IP address and default gateway. For the switch host address, you should use the last available IP address on the management subnet. In addition, the switch needs to be configured to be in the same VTP domain as the building_1 switch and also needs to be configured as a VTP client. Assume that the IP configuration and VTP configuration on building_1 are complete and correct. The configuration of the router is not accessible for this exercise. You must accomplish the following tasks:
Determine and configure the IP host address of the new switch. Determine and configure the default gateway of the new switch. Determine and configure the correct VTP domain name for the new switch.
Configure the new switch as a VTP client.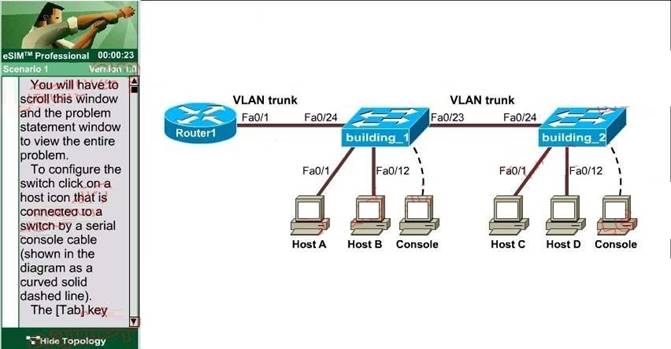
Correct Answer:
HerearetheStepsforthisLabSolution:
The question states we can't access the router so we can only get required information from switch building_1. Click on the PC connected with switch building_1 (through a console line) to access switch building_1s CLI. On this switch use the show running-config command:
building_1#show running-config
Next use the show vtp status command to learn about the vtp domain on this switch building_1#show vtp status
(Notice: the IP address, IP default-gateway and VTP domain name might be different!!!) You should write down these 3 parameters carefully.
Configuring the new switch
+ Determine and configure the IP host address of the new switch The question requires "for the switch host address, you should use the last available IP address on the management subnet". The building_1 switch's IP address, which is 192.168.22.50 255.255.255.224, belongs to the management subnet.
Increment: 32 (because 224 = 1110 0000)
Network address: 192.168.22.32
Broadcast address: 192.168.22.63
->The last available IP address on the management subnet is 192.168.22.62 and it hasn't been used (notice that the IP address of Fa0/1 interface of the router is also the default gateway address 192.168.22.35).
Also notice that the management IP address of a switch should be configured in Vlan1 interface. After it is configured, we can connect to it via telnet or SSH to manage it. Switch2#configure terminal
Switch2(config)#interface Vlan1
Switch2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.22.62 255.255.255.224
Switch2(config-if)#no shutdown (not really necessary since VLAN interfaces are not physical and are not shut
down but, no harm in doing so and is good practice for physical ports)
+ Determine and configure the default gateway of the new switch The default gateway of this new switch is same as that of building_1 switch, which is 192.168.22.35 Switch2(config-if)#exit
Switch2(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.22.35
+ Determine and configure the correct VTP domain name for the new switch The VTP domain name shown on building_1 switch is Cisco so we have to use it in the new switch (notice: the VTP domain name will be different in the exam and it is case sensitive so be careful)
Switch2(config)#vtp domain Cisco
+ Configure the new switch as a VTP client Switch2(config)#vtp mode client
We should check the new configuration with the "show running-config" & "show vtp status"; also try pinging from the new switch to the the default gateway to make sure it works well. Finally save the configuration:
Switch2(config)#exit
Switch2#copy running-config startup-config

